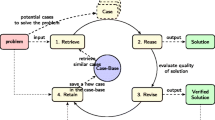
Abstract
An essential issue for developing analogical reasoning systems (such as Case-Based Reasoning systems) is to build the case memory by selecting registers from an external database. This issue is called case selection and the literature provides a wealth of algorithms to deal with it. For any particular domain, to choose the case selection algorithm is a critical decision on the system design. Despite some algorithms obtain good results, a specific algorithms evaluation is needed. Most of the efforts done in this line focus on the number of registers selected and providing a simple evaluation of the system obtained. In some domains, however, the system must fulfil certain constraints related to accuracy or efficiency. For instance, in the medical field, specificity and sensitivity are critical values for some tests. In order to partially solve this problem, we propose an evaluation methodology to obtain the best case selection method for a given memory case. In order to demonstrate the usefulness of this methodology, we present new case selection algorithms based on evolutionary multi-objective optimization. We compare the classical algorithms and the multi-objective approach in order to select the most suitable case selection algorithm according to different standard problems.
This study was partially financed by the Spanish MEC through projects TIN2009-14372-C03-01 and PET2007-0033 and the regional project SENECA 15277/PI/10.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aamodt, A., Plaza, E.: Case-based reasoning: Foundational issues, methodological variations, and system approaches. AI Communications 7, 39–59 (1994)
Aha, D.W.: Tolerating noisy, irrelevant and novel attributes in instance-based learning algorithms. International Journal Of Man-Machine Studies 36, 267–287 (1992)
Aha, D.W., Kiblerand, D., Albert, M.K.: Instance-based learning algorithms. Machine Learning 6, 37–66 (1991)
Ahn, H., Kim, K., Han, I.: A case-based reasoning system with the two-dimensional reduction technique for customer classification. Expert Systems With Applications 32, 1011–1019 (2007)
Chang, C.L.: Finding prototypes for nearest neighbor classifiers. IEEE Transactions on Computers C23, 1179–1184 (1974)
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., Meyarivan, T.: A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 6, 182–197 (2002)
Gates, G.W.: The reduced nearest neighbor rule. IEEE Transactions On Information Theory 18, 431–433 (1972)
Hall, R.P.: Computational approaches to analogical reasoning. Artificial Intelligence 39, 39–120 (1989)
Hart, P.E.: The condensed nearest neighbor rule. IEEE Transaction On Information Theory 14, 515–516 (1968)
Jara, A., Martinez, R., Vigueras, D., Sanchez, G., Jimenez, F.: Attribute selection by multiobjective evolutionary computation applied to mortality from infection severe burns patients. In: Proceedings of the International Conference of Health Informatics (HEALTHINF 2011), Algarbe, Portugal, pp. 467–471 (2011)
Kibler, D., Aha, D.W.: Learning representative exemplars of concepts: An initial case study. In: Proceedings of the Fourth International Workshop on Machine Learning, pp. 24–30 (1987)
Kling, R.E.: A paradigm for reasoning by analogy. Artificial Intelligence (2),147–148 (1971)
Kolodner, J.L.: Making the Implicit Explicit: Clarifying the Principles of Case-Based Reasoning. In: Case-based Reasoning: Experiences, Lessons and Future Directions, ch. 16, pp. 349–370. AAAI, Menlo Park (1996)
Kuncheva, L.I., Jain, L.C.: Nearest neighbor classifier: Simultaneous editing and feature selection. Pattern Recognition Letters 20, 1149–1156 (1999)
Leake, D.B., Wilson, D.C.: Categorizing case-base maintenance: Dimensions and directions. In: Smyth, B., Cunningham, P. (eds.) EWCBR 1998. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 1488, pp. 196–207. Springer, Heidelberg (1998)
McKenna, E., Smyth, B.: Competence-guided case-base editing techniques. In: Blanzieri, E., Portinale, L. (eds.) EWCBR 2000. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 1898, pp. 186–197. Springer, Heidelberg (2000)
McSherry, D.: Automating case selection in the construction of a case library. Knowledge-Based Systems 13, 133–140 (2000)
Montani, S., Portinale, L., Leonardi, G., Bellazzi, R., Bellazzi, R.: Case-based retrieval to support the treatment of end stage renal failure patients. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 37(1), 31–42 (2006)
Nersessian, N.: The cognitive basis of model-based reasoning in science. In: The Cognitive Basis of Science, ch. 7, pp. 133–153. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2002)
Olsson, E., Funk, P., Xiong, N.: Fault diagnosis in industry using sensor readings and case-based reasoning. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems 15(1), 41–46 (2004)
Pan, R., Yang, Q., Pan, S.J.: Mining competent case bases for case-based reasoning. Artificial Intelligence 171, 1039–1068 (2007)
Ritter, G.L., Woodruff, H.B., Lowry, S.R., Isenhour, T.L.: Algorithm for a selective nearest neighbor decision rule. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 21, 665–669 (1975)
Smyth, B., Keane, M.T.: Remembering to forget - A competence-preserving case deletion policy for case-based reasoning systems. In: Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI 1995), August 20-25, vol. 1 and 2, pp. 377–382 (1995)
Smyth, B., McKenna, E.: Modelling the competence of case-bases. In: Smyth, B., Cunningham, P. (eds.) EWCBR 1998. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 1488, pp. 208–220. Springer, Heidelberg (1998)
Smyth, B., McKenna, E.: Building compact competent case-bases. In: Althoff, K.-D., Bergmann, R., Branting, L.K. (eds.) ICCBR 1999. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 1650, pp. 329–342. Springer, Heidelberg (1999)
Smyth, B., McKenna, E.: Competence models and the maintenance problem. Computational Intelligence 17, 235–249 (2001)
Tomek, I.: An experiment with the edited nearest-neighbor rule. IEEE Transactions On Systems Man and Cybernetics 6, 448–452 (1976)
Watson, I.: Case-based reasoning is a methodology not a technology. Knowledge-Based Systems 12, 303–308 (1999)
Wilson, D.L.: Asymptotic properties of nearest neighbor rules using edited data. IEEE Transactions On Systems Man and Cybernetics SMC 2, 408–420 (1972)
Wilson, D.R., Martinez, T.R.: Instance pruning techniques. In: Machine Learning: Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference (ICML 1997), pp. 404–411. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (1997)
Wilson, D.R., Martinez, T.R.: Reduction techniques for instance-based learning algorithms. Machine Learning 38, 257–286 (2000)
Winston, P.H.: Learning and reasoning by analogy. Commun. ACM 23, 689–703 (1980)
Zitzler, E., Laumanns, M., Thiele, L.: SPEA2: Improving the strength pareto evolutionary algorithm for multiobjective optimization. In: Evolutionary Methods for Design Optimization and Control with Applications to Industrial Problems, Athens, Greece, pp. 95–100. International Center for Numerical Methods in Engineering (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lupiani, E., Juarez, J.M., Jimenez, F., Palma, J. (2011). Evaluating Case Selection Algorithms for Analogical Reasoning Systems. In: Ferrández, J.M., Álvarez Sánchez, J.R., de la Paz, F., Toledo, F.J. (eds) Foundations on Natural and Artificial Computation. IWINAC 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6686. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21344-1_36
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21344-1_36
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-21343-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-21344-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)