Abstract
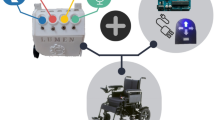
The importance of natural interaction increases when the subjects are disabled people. It has been found that embedded solutions for impaired people lack in fluid interaction properties. This work investigates the interface design of a wheelchair controller according to the rules of physicality. Our aim is to provide further ease of use to the impaired whilst strengthening link between embedded software engineering and human-computer interaction. We propose an improved multi-function interface design by using Nintendo’s Wiimote that is more intuitive, robust, low cost, and most importantly, natural to use.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dix, A., Ghazali, M., Ramduny-Ellis, D.: Modelling Devices for Natural Interaction. Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science 23–40 (2008)
Ghazali, M., Dix, A.: Visceral Interaction. In: Proceeding of The British Computer Society BCS-HCL, pp. 68–72. Edinburgh, Scotland (2005)
Norman, D.: The next UI breakthrough, part 2: physicality. Interactions 14(4), 46–47 (2007)
Sharp, H., Robinson, H., Petre, M.: The role of physical artefacts in agile software development: Two complementary perspectives. Interacting with Computers 21(1-2), (Special issue: Enactive Interfaces) 108–116 (2009)
Nomura, S., Hutchins, E., Holder, B.E.: The uses of paper in commercial airline flight operations. In: CSCW 2006, pp. 249–258 (2006)
Sellen, A.J., Harper, R.H.R.: The Myth of the Paperless Office. The MIT Press, Cambridge (2003)
IterEx., http://www.planningcards.com/site/
Bujnowski, A., Drozd, M., Kowalik, R., Wtorek, J.: A tactile system for informing the blind on direction of a walk. In: Conference on Human System Interactions, pp. 893–897 (2008)
Hara, M., Shokur, S., Yamamoto, A., Higuchi, T., Gassert, R., Bleuler, H.: Virtual environment to evaluate multimodal feedback strategies for augmented navigation of the visually impaired. In: Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 975–978 (2010)
Shah, C., Bouzit, M., Youssef, M., Vasquez, L.: Evaluation of RU-Netra - Tactile Feedback Navigation System For The Visually Impaired. In: International Workshop on Virtual Rehabilitation, pp. 72–77 (2006)
Ivanchenko, V., Coughlan, J., Gerrey, W., Shen, H.: Computer vision-based clear path guidance for blind wheelchair users. In: Proceedings of the 10th international ACM SIGACCESS conference on Computers and accessibility (Assets 2008), pp. 291–292. ACM, New York (2008)
Kuno, Y., Yoshimura, T., Mitani, M., Nakamura, A.: Robotic wheelchair looking at all people with multiple sensors. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems, pp. 341–346 (2003)
Abascal, J., Cagigas, D., Garay, N., Gardeazabal, L.: Mobile Interface for a Smart Wheelchair. In: Paternó, F. (ed.) Mobile HCI 2002. LNCS, vol. 2411, pp. 373–377. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Home Care Specialists Inc., http://www.homecarespecialistsinc.com/medical_equipment.html
Sabil, S., Jawawi, D.N.A.: MARMOT and PECOS Hybrid Approach for Embedded Real Time Software Development. In: The 5th International Conference on Information & Communication Technology and Systems (ICTS 2009), Surabaya, Indonesia (2009)
Dix, A., Ghazali, M., Gill, S., Hare, J., Ramduny-Ellis, D.: Physigrams: Modelling Devices for Natural Interaction. Formal Aspects of Computing 21(6), 613 (2009)
Ghazali, M.: Discovering Natural Interaction of Physical Qualities to Design Fluid Interaction for Novel Devices. Research Monograph, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (2007)
Tech Watch, http://www.techwatch.co.uk/2010/10/04/one-in-three-uk-households-own-a-nintendo-wii/
Game Spot Asia, http://asia.gamespot.com/users/MushroomWig/show_blog_entry.php?topic_id=m-100-25803446
Standen, P.J., Camm, C., Battersby, S., Brown, D.J., Harrison, M.: An evaluation of the Wii Nunchuk as an alternative assistive device for people with intellectual and physical disabilities using switch controlled software. Computers & Education 56(1), 2–10 (2011), Serious Games
Shih, C., Chang, M., Shih, C.: A limb action detector enabling people with multiple disabilities to control environmental stimulation through limb action with a Nintendo Wii Remote Controller. Research in Developmental Disabilities 31(5), 1047–1053 (2010)
Raza, S.A., Ahmed, M.W., Madni, T.M., Tahir, M., Khan, M.I., Ashraf, M.: Preliminary evaluation of 3D unistroke gestures: An accelerometer-based approach. In: IEEE ICIIT, vol. 1, pp. 634–638. University of Central Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan (2010)
Olufs, S., Vincze, M.: Simple inexpensive interface for robots using the Nintendo Wii controller. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ international conference on Intelligent robots and systems (IROS 2009), pp. 473–479. IEEE Press, Piscataway (2009)
Kim, W.Y., Son, H.S., Kim, R.Y.C., Jeon, B.K.: User Behavior Analysis Framework (UBAF):Mapping HCI with SE. In: Future Generation Communication and Networking (FGCN 2007), vol. 2, pp. 565–568. IEEE Computer Society Press, Washington DC, USA (2007)
Dix, A., Finlay, J., Abowd, G., Beale, R.: Human-Computer Interaction, 3rd edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ashraf, M., Ghazali, M. (2011). Towards Natural Interaction with Wheelchair Using Nintendo Wiimote Controller. In: Zain, J.M., Wan Mohd, W.M.b., El-Qawasmeh, E. (eds) Software Engineering and Computer Systems. ICSECS 2011. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 181. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-22203-0_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-22203-0_20
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-22202-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-22203-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)