Abstract
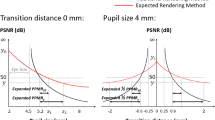
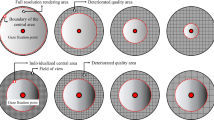
This paper presents gaze-dependent depth-of-field (DOF) rendering setup, consisting of high frequency eye tracker connected to a graphics workstation. A scene is rendered and visualised with the DOF simulation controlled by data captured with the eye tracker. To render a scene in real-time, the reverse-mapped z-buffer DOF simulation technique with the blurring method based on Poisson disk is used. We conduct perceptual experiments to test human impressions caused by simulation of the DOF phenomenon and to assess benefits of using eye tracker to control the DOF effect rendering in virtual environments. Additionally, we survey the eye tracking technologies suitable for virtual environments and preview techniques of the real time DOF rendering.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marks, S., Windsor, J., Wünsche, B.: Evaluation of game engines for simulated surgical training. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques in Australia and Southeast Asia, GRAPHITE 2007, pp. 273–280 (2007)
Anderson, E.F., McLoughlin, L., Liarokapis, F., Peters, C., Petridis, P., Freitas, S.: Serious Games in Cultural Heritage VAST 2009: 10th International Symposium on Virtual Reality, Archaeology and Cultural Heritage - VAST-STAR, Short and Project Proceedings, pp. 29-48 (2009)
Myers, S.: Streamlining Simulation Development using a Commercial Game Engine Camber Corporation, Technical Report RTO-MP-MSG-069
Ritterfeld, U., Cody, M., Vorderer, P.: Serious Games: Mechanisms and Effects, 1st edn. Routledge, New York (2009)
Goldstein, E.B.: Sensation and Perception, 5th edn. Brooks/Cole Publishing Company (1998)
Mather, G.: The use of image blur as a depth cue. Perception 26, 1147–1158 (1997)
Hillaire, S., Lecuyer, A., Cozot, R., Casiez, G.: Using an eye-tracking system to improve camera motions and depth-of-field blur effects in virtual environments. In: Proc. of IEEE Virtual Reality, pp. 47–50 (2008)
Duchowski, A.T.: Eye Tracking Methodology: Theory and Practice, 2nd edn. Springer, London (2007)
RED250 Technical Specification. SensoMotoric Instruments GmbH (2009)
Tobii T/X series Eye Trackers. Product Description. Tobii Technology AB, 2nd edn. (2009)
Morimoto, C.H., Mimica, M.: Eye gaze tracking techniques for interactive applications. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 98(1), 4–24 (2005)
Demers, J.: Depth of Field: A Survey of Techniques GPU GEMS. Addison-Wesley, Reading (2004)
Riguer, G., Tatarchuk, N., Isidoro, J.: Real-time depth of field simulation. haderX2: Shader Programming Tips and Tricks with DirectX 9.0, 529–579 (2002)
Potmesil, M., Chakravarty, I.: Modeling motion blur in computer-generated images. ACM SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 17(3), 389–399 (1983)
Hillaire, S., Lecuyer, A., Cozot, R., Casiez, G.: Depth-of-field blur effects for first-person navigation in virtual environments. In: Proc. of the ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology, pp. 203–206 (2007)
Hammon, E.: Practical post-process depth of field. GPU Gems 3, Hubert Nguyen, NVIDIA Corporation (2008)
Poole, A., Ball, L.J.: Eye Tracking in Human-Computer Interaction and Usability Research: Current Status and Future Prospects. Encyclopedia of Human-Computer Interaction, C. Ghaoui, Idea Group, Inc., Pennsylvania (2005)
Sasse, D.: A Framework for Psychophysiological Data Acquisition in Digital Games Master’s thesis (2008)
Lee, S., Eisemann, E., Seidel, H.P.: Real-Time Lens Blur Effects and Focus Control. ACM Transactions on Graphics, SIGGRAPH 2010 (2010)
Lee, S., Eisemann, E., Seidel, H.P.: Depth-of-Field Rendering with Multiview Synthesis. ACM Trans. Graph (SIGGRAPH ASIA 2009) 28(5), 1–6 (2009)
Lee, S., Kim, G.J., Choi, S.: Real-Time Depth-of-Field Rendering Using Splatting on Per-Pixel Layers. Computer Graphics Forum 27(7), 1955–1962 (2008)
Aknine-Moller, T., Haines, E., Hoffman, N.: Real Time Rendering, 3rd edn. A K Peters, Stanford (2008)
ITU-R.REC.BT.500-11: Methodology for the subjective assessment of the quality for television pictures (2002)
Slater, M., Spanlang, B., Corominas, D.: Simulating virtual environments within virtual environments as the basis for a psychophysics of presence. ACM Trans. Graph. 29(4), 92:1–02:9. (2010)
Slater, M.: Place illusion and plausibility can lead to realistic behaviour in immersive virtual environments. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 364(1535), 3549–3557 (2009)
Hillaire, S., Lécuyer, A., Regia-Corte, T., Cozot, R., Royan, J., Breton, G.: A real-time visual attention model for predicting gaze point during first-person exploration of virtual environments. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology (VRST 2010), Hong Kong, pp. 191–198 (2010)
Kenny, A., Delaney, H., Mcloone, S., Ward, T.: A preliminary investigation into eye gaze data in a first person shooter game. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Modelling and Simulation. Addison-Wesley, Reading (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mantiuk, R., Bazyluk, B., Tomaszewska, A. (2011). Gaze-Dependent Depth-of-Field Effect Rendering in Virtual Environments. In: Ma, M., Fradinho Oliveira, M., Madeiras Pereira, J. (eds) Serious Games Development and Applications. SGDA 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6944. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23834-5_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23834-5_1
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-23833-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-23834-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)