Abstract
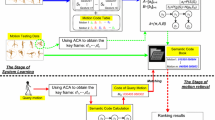
In recent years, with the development and increasingly mature of motion capture technology, it has become one of the most widely used technologies to obtain realistic human motion in computer animation. With the increasing demands, motion dataset is becoming larger and larger. Due to motion feature data have the high-dimensional complexity, we first adopt nonlinear ISOMAP manifold learning algorithm to resolve the “curse of dimensionality” problem for motion feature data. In order to save the time of reducing dimension, we adopt the scarcity of neighboring-graph to improve ISOMAP algorithm for making it apply the massive human motion database. Then we build a motion string index for database, deploy Smith-Waterman algorithm to compare the retrieval samples’ motion string with motion strings of candidate datasets, finally, we obtain the similar motion sequence. Experiment results show that the approach proposed in this paper is effective and efficient.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shuangyuan, W., Shihong, X., Zhaoqi, W.: Efficient motion data indexing and retrieval with local similarity measure of motion strings. Vis. Computer 25, 499–508 (2009)
Lin, Y.: Efficient Motion Search in Large Motion Capture Databases. In: Bebis, G., Boyle, R., Parvin, B., Koracin, D., Remagnino, P., Nefian, A., Meenakshisundaram, G., Pascucci, V., Zara, J., Molineros, J., Theisel, H., Malzbender, T. (eds.) ISVC 2006. LNCS, vol. 4291, pp. 151–160. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Yamasaki, T., Aizawa, K.: Content-Based Cross Search for Human Motion Data Using Time-Varying Mesh and Motion Capture Data. In: Proceeding of IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, ICME 2007, Beijing, China, pp. 2007–2009 (2007)
Muller, M., Roder, T., Clausen, M.: Efficient Content-Based Retrieval of Motion Capture Data. ACM Transactions on Graphics 24(3), 677–685 (2005)
Gao, Y., Ma, L., Chen, Y., Liu, J.: Content-Based Human Motion Retrieval with Automatic Transition. In: Nishita, T., Peng, Q., Seidel, H.-P. (eds.) CGI 2006. LNCS, vol. 4035, pp. 360–371. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Gu, Q., Peng, J., Deng, Z.: Compressions of human motion capture data using motion pattern indexing. Compute Graph Forum 28(1), 1–12 (2009)
Sonoda, M., Tsuruta, S., Yoshimura, M., Hachimura, K.: Segmentation of dancing movement by extracting features from motion capture data. Journal of the Institute of Image Electronics Engineers of Japan 37(3), 303–311 (2008)
Jian, X., Tongqiang, G., Tingyue, Z., Lv, Y.: Based on two reference index large human motion database index (in Chinese). Journal of Computer Research and Development 45(12), 2145–2153 (2008)
Pradhan, G.N., Li, C., Prabhakaran, B.: Hierarchical Indexing Structure for 3D Human Motions. In: Cham, T.-J., Cai, J., Dorai, C., Rajan, D., Chua, T.-S., Chia, L.-T. (eds.) MMM 2007, Part I. LNCS, vol. 4351, pp. 386–396. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Gaurav, N.P., Balakrishnan, P.: Indexing 3D Human Motion Repositories for Content-Based Retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine 13(5), 802–809 (2009)
Zhigang, D., Qin, G., Qing, L.: Perceptually Consistent Example-based Human Motion Retrieval. In: I3D 2009, Boston, Massachusetts, Boston, Massachusetts, February 27-March 1, pp. 191–198. ACM, New York (2009)
Choensawat, W., Choi, W., Hachimura, K.: A quick filtering for similarity queries in motion capture databases. In: Muneesawang, P., Wu, F., Kumazawa, I., Roeksabutr, A., Liao, M., Tang, X. (eds.) PCM 2009. LNCS, vol. 5879, pp. 404–415. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Guo, X., Zhang, Q., Liu, R., Zhou, D., Dong, J. (2011). 3D Human Motion Retrieval Based on ISOMAP Dimension Reduction. In: Deng, H., Miao, D., Lei, J., Wang, F.L. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Computational Intelligence. AICI 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 7004. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23896-3_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23896-3_19
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-23895-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-23896-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)