Abstract
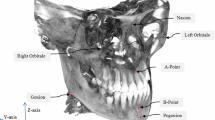
In this paper an automated method is presented for the localization of cephalometric landmarks in craniofacial cone-beam computed tomography images. This method makes use of a statistical sparse appearance and shape model obtained from training data. The sparse appearance model captures local image intensity patterns around each landmark. The sparse shape model, on the other hand, is constructed by embedding the landmarks in a graph. The edges of this graph represent pairwise spatial dependencies between landmarks, hence leading to a sparse shape model. The edges connecting different landmarks are defined in an automated way based on the intrinsic topology present in the training data. A maximum a posteriori approach is employed to obtain an energy function. To minimize this energy function, the problem is discretized by considering a finite set of candidate locations for each landmark, leading to a labeling problem. Using a leave-one-out approach on the training data the overall accuracy of the method is assessed. The mean and median error values for all landmarks are equal to 2.41 \(\textrm{mm}\) and 1.49 \(\textrm{mm}\), respectively, demonstrating a clear improvement over previously published methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swennen, G.R.J., Schutyser, F., Hausamen, J.-E.: Three-Dimensional Cephalometry, A Color Atlas and Manual. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Swennen, G.R.J., Schutyser, F., Barth, E.L., De Groeve, P., De Mey, A.: A New Method of 3-D Cephalometry Part I: The Anatomic Cartesian 3-D Reference System. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 17(2), 314–325 (2006)
Leonardi, R., Giordano, D., Maiorana, F., Spampinato, C.: Automatic Cephalometric Analysis. Angle Orthod. 78(1), 145–151 (2009)
Keustermans, J., Mollemans, W., Vandermeulen, D., Suetens, P.: Automated Cephalometric Landmark Identification using a Local Shape and Appearance Model. In: Proc. ICPR (2010)
Cheung, W., Hamarneh, G.: n-SIFT: n-dimensional scale invariant feature transform. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 18(9), 2012–2021 (2009)
Schölkopf, B., Smola, A., Müller, K.R.: Nonlinear component analysis as a kernel eigenvalue problem. Neural Computation 10, 1299–1319 (1998)
Davies, R.H., Twining, C.J., Cootes, T.F., Waterton, J.C., Taylor, C.J.: A minimum description length approach to statistical shape modelling. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 21(5), 525–537 (2002)
Thodberg, H.H.: Minimum description length shape and appearance models. In: Taylor, C.J., Noble, J.A. (eds.) IPMI 2003. LNCS, vol. 2732, pp. 51–62. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Langs, G., Paragios, N.: Modeling the structure of multivariate manifolds: Shape maps. In: Proc. CVPR (2008)
Boykov, Y., Veksler, O., Zabih, R.: Fast Approximate Energy Minimization via Graph Cuts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 23(11), 1222–1239 (2001)
Wainwright, M.J., Jaakkola, T.S., Willsky, A.S.: MAP Estimation Via Agreement on Trees: Message-Passing and Linear Programming. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 51(11), 3697–3717 (2006)
Kolmogorov, V.: Convergent Tree-reweighted Message Passing for Energy Minimization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 28(10), 1568–1583 (2006)
Kolmogorov, V., Zabih, R.: What Energy Functions Can Be Minimized via Graph Cuts? IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26(2), 147–159 (2001)
Lempitsky, V., Rother, C., Roth, S., Blake, A.: Fusion Moves for Markov Random Field Optimization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(8), 1392–1405 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Keustermans, J., Smeets, D., Vandermeulen, D., Suetens, P. (2011). Automated Cephalometric Landmark Localization Using Sparse Shape and Appearance Models. In: Suzuki, K., Wang, F., Shen, D., Yan, P. (eds) Machine Learning in Medical Imaging. MLMI 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7009. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24319-6_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24319-6_31
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-24318-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-24319-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)