Abstract
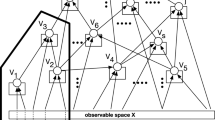
Qualitative propagation influences in qualitative inferences are unlike and interrelated on the different hierarchy of knowledge granules, and quantitative information loss easily results in reasoning conflicts. This paper presents a hierarchical qualitative inference model with substructures which to some extent can eliminate the qualitative impact of uncertainty and solve trade-off problems by metastructures with basic decomposition and coarse-grained mesoscale substructures with edge-deletion. The substructural inferences could not only reduce computational complexity, but provide an approximate strategy for modular reasoning on large-scale problems. The example respectively illustrates the two substructural methods are both effective.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi, A., Darwiche, A.: A Variational Approach for Approximating Bayesian networks by edge deletion. In: Proceedings of the 22nd Conf. UAI, pp. 80–89 (2006)
Druzdzel, M.J., Henrion, M.: Efficient Reasoning in Qualitative Probabilistic Networks. In: 11st National Conference on AAAI, pp. 548–553 (1993)
Feng, Q., Miao, D., Cheng, Y.: Hierarchical decision rules mining. Expert Systems with Applications 37(3), 2081–2091 (2010)
Li, X., Liao, S.: Hierarchical Reasoning in QPNs based on Network Decomposition. In: IEEE International Conference on ICIP, pp. 97–100 (2010)
Liu, C.L., Wellman, M.P.: Incremental Trade-off Resolution in Qualitative Probabilistic Networks. In: Proc. of Conf. UAI, pp. 338–345 (1998)
Pearl, J.: Probabilistic Reasoning in Intelligent Systems: Networks of Plausible Inference. Morgan Kaufmann, Palo Alto (1988)
Pedrycz, W.: Hierarchies of Architectures of Collaborative Computational Intelligence. International Journal of Software Science and Computational Intelligence, 18–31 (2009)
Renooij, S., van der Gaag, L.C., Parsons, S., Green, S.: Pivotal Pruning of Trade-offs in QPNs. In: Proc. of Conf. UAI, pp. 515–522 (2000)
Renooij, S., van der Gaag, L.C., Parsons, S.: Context-specific Sign-propagation in Qualitative Probabilistic Networks. Artificial Intelligence 144(1), 207–230 (2002)
Renooij, S., van der Gaag, L.C.: Enhanced qualitative probabilistic networks for resolving trade-offs. Artificial Intelligence 172(12-13), 1470–1494 (2008)
Renooij, S.: Bayesian network sensitivity to arc-removal. In: Proceedings of the Fifth European Workshop on Probabilistic Graphical Models, pp. 233–240 (2010)
Van Kouwen, F.A., Renooij, S., Schot, P.: Inference in Qualitative Probabilistic Networks revisited. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 50(5), 708–720 (2009)
Wellman, M.P.: Fundamental Concepts of Qualitative Probabilistic Networks. Artificial Intelligence 44, 257–303 (1990)
Yao, J.T.: A ten-year review of granular computing. In: Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Granular Computing, San Jose, USA, pp. 734–739 (2007)
Yao, Y.Y.: Integrative Levels of Granularity. In: Bargiela, A., Pedrycz, W. (eds.) Human-Centric Information Processing Through Granular Modeling, pp. 31–47. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Yue, K., Liu, W.: Qualitative probabilistic networks with rough-set-based weights. In: Proc. of ICMLC, vol. 3, pp. 1768–1774 (2008)
Yue, K., Liu, W., Yue, M.: Quantifying Influences in the Qualitative Probabilistic Network with Interval Probability Parameters. Applied Soft. Computing 11, 1135–1143 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, Z., Miao, D., Qian, J. (2011). Hierarchical Qualitative Inference Model with Substructures. In: Yao, J., Ramanna, S., Wang, G., Suraj, Z. (eds) Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology. RSKT 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 6954. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24425-4_94
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24425-4_94
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-24424-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-24425-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)