Abstract
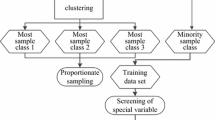
Credit client scoring on medium sized data sets can be accomplished by means of Support Vector Machines (SVM), a powerful and robust machine learning method. However, real life credit client data sets are usually huge, containing up to hundred thousands of records, with good credit clients vastly outnumbering the defaulting ones. Such data pose severe computational barriers for SVM and other kernel methods, especially if all pairwise data point similarities are requested. Hence, methods which avoid extensive training on the complete data are in high demand. A possible solution is clustering as preprocessing and classification on the more informative resulting data like cluster centers. Clustering variants which avoid the computation of all pairwise similarities robustly filter useful information from the large imbalanced credit client data set, especially when used in conjunction with a symbolic cluster representation. Subsequently, we construct credit client clusters representing both client classes, which are then used for training a non standard SVM adaptable to our imbalanced class set sizes. We also show that SVM trained on symbolic cluster centers result in classification models, which outperform traditional statistical models as well as SVM trained on all our original data.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basu S, Davidson I, Wagstaff K (2009) Constrained clustering: Advances in algorithms, theory, and applications. Data mining and knowledge discovery series. Chapman Hall/CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Billard L, Diday E (2006) Symbolic data analysis. Wiley, New York
Bock HH, Diday E (2000) Analysis of symbolic data: Exploratory methods for extracting statistical information from complex data. Springer, Berlin
Chan PK, Stolfo SJ (2001) Toward scalable learning with non-uniform class and cost distributions: A case study in credit card fraud detection. In: Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp 164–168
Durand D (1941) Risk elements in consumer installment financing. National Bureau of Economic Research, New York
Evgeniou T, Pontil M (2002) Support vector machines with clustering for training with very large datasets. Lect Notes Artif Intell 2308:346–354
Hanley A, McNeil B (1982) The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve. Diagn Radiol 143:29–36
Jain AK, Murty MN, Flynn PJ (1999) Data clustering: A review. ACM Comput Surv 31(3):264–323
Li B, Chi M, Fan J, Xue X (2007) Support cluster machine. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, pp 505–512
Lin Y, Lee Y, Wahba G (2002) Support vector machines for classification in nonstandard situations. Mach Learn 46(1–3):191–202
MacQueen JB (1967) Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In: Proceedings of the Fifth Symposium on Math, Statistics and Probability, University of California Press, Berkeley, CA, pp 281–297
Stecking R, Schebesch KB (2006) Variable subset selection for credit scoring with support vector machines. In: Haasis HD, Kopfer H, Schönberger J (eds) Operations research proceedings. Springer, Berlin, pp 251–256
Stecking R, Schebesch KB (2009) Clustering large credit client data sets for classification with SVM. In: Credit Scoring and Credit Control XI Conference, CRC Edinburgh, p 15 ff.
Thomas LC, Oliver RW, Hand DJ (2005) A survey of the issues in consumer credit modelling research. J Oper Res Soc 56(9):1006–1015
Wang Y, Zhang X, Wang S, Lai KK (2008) Nonlinear clustering–based support vector machine for large data sets. Optim Meth Software Math Programm Data Mining and Machine Learning 23(4):533–549
Weiss GM (2004) Mining with rarity: A unifying framework. SIGKDD Explorations 6(1):7–19
Yu H, Yang J, Han J (2003) Classifying large data sets using SVMs with hierarchical clusters. In: Proceedings of the ninth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, ACM, New York, KDD ’03, pp 306–315
Yuan J, Li J, Zhang B (2006) Learning concepts from large scale imbalanced data sets using support cluster machines. In: Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia. ACM, New York, pp 441–450
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Stecking, R., Schebesch, K.B. (2012). Classification of Large Imbalanced Credit Client Data with Cluster Based SVM. In: Gaul, W., Geyer-Schulz, A., Schmidt-Thieme, L., Kunze, J. (eds) Challenges at the Interface of Data Analysis, Computer Science, and Optimization. Studies in Classification, Data Analysis, and Knowledge Organization. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24466-7_45
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24466-7_45
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-24465-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-24466-7
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)