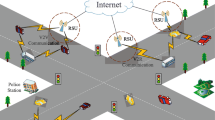
Abstract
For a long term of vehicle communication research, now VANET is in a stage of implementation. However, most of VANET researches focus on message transmission. Vehicle is extremely personal device; therefore personal information, so called privacy has to be protected. In this paper, we analyze identity and location privacy threatening factors, problems, and solutions based on network model. To analyze solution’s effectiveness, we define four attack models: External attack, Internal attack, Correlational attack, and Relational attack. According to our research, most of the solutions use pseudonym identity or address changing scheme to protect identity privacy. Also, solutions are weak to or do not consider the relational attack. We analyze this is due the meet the network model’s transparency design goal and protect vehicle’s real identity even revealing the vehicle’s location. The result of this paper could guide a way to design a privacy preserve solution and present a trend of existing solutions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kent, S.T., Millett, L.I.: IDs–not that easy: Questions about nationwide identity systems. Natl. Academy Pr., Washington DC (2002)
Beresford, A.R., Stajano, F.: Location Privacy in Pervasive Computing. IEEE Pervasive Computing 2, 46–55 (2005)
Fuentes, J.M., González-Tablas, A.I., Ribagorda, A.: Overview of Security Issues in Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks (2010)
Gruteser, M., Grunwald, D.: Enhancing Location Privacy in Wireless LAN through Disposable Interface Identifiers: A Quantitative Analysis. Mobile Networks and Applications 10, 315–325 (2005)
Huang, L., Matsuura, K., Yamane, H., Sezaki, K.: Enhancing wireless location privacy using silent period. In: IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, 2005, vol. 2, pp. 1187–1192. IEEE, Los Alamitos (2005)
Jiang, T., Wang, H.J., Hu, Y.C.: Preserving location privacy in wireless LANs. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications and Services, pp. 246–257. ACM, New York (2007)
Pang, J., Greenstein, B., Gummadi, R., Seshan, S., Wetherall, D.: 802.11 user fingerprinting. In: Proceedings of the 13th Annual ACM International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, pp. 99–110. ACM, New York (2007)
Greenstein, B., McCoy, D., Pang, J., Kohno, T., Seshan, S., Wetherall, D.: Improving wireless privacy with an identifier-free link layer protocol. In: Proceeding of the 6th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, pp. 17–20. Citeseer (June 2008)
Droms, R.: Dynamic host configuration protocol (1997)
Srisuresh, P., Holdrege, M.: RFC 2663. IP Network Address Translator (NAT) Terminology and Considerations (1999)
Thomson, S., Narten, T., Jinmei, T.: RFC4862: IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration. Standards Track, http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc4862.txt AUTOCONF-Stating the Problem, 31
Haddad, W., Nordmark, E., Dupontand, F., Bagnulo, M., Park, S., Patil, B.: Privacy for Mobile and Multi-homed Nodes: MoMiPriv Problem Statement (2005)
Groat, S., Dunlop, M., Marchany, R., Tront, J.: The privacy implications of stateless IPv6 addressing. In: Proceedings of the Sixth Annual Workshop on Cyber Security and Information Intelligence Research, pp. 1–4. ACM, New York (2010)
Lindqvist, J.: IPv6 is Bad for Your Privacy (2007)
Trostle, J., Matsuoka, H., Tariq, M.M.B., Kempf, J., Kawahara, T., Jain, R.: Cryptographically protected prefixes for location privacy in ipv6. In: Martin, D., Serjantov, A. (eds.) PET 2004. LNCS, vol. 3424, pp. 142–166. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Narten, T., Draves, R., Krishnan, S.: RFC 4941-Privacy Extensions for Stateless Address Autoconfiguration in IPv6. IETF (September 2007)
Nikander, P., Arkko, J., Kempf, J., Zill, B.: SEcure Neighbor Discovery (SEND)
Droms, R., Bound, J., Volz, B., Lemon, T., Perkins, C., Carney, M.: Dynamic host configuration protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) (2003)
Koodli, R.: RFC 4882: IP Address Location Privacy and Mobile IPv6: Problem Statement (2007)
Qiu, Y.: RFC 5726 : Mobile IPv6 Location Privacy Solutions (2010)
Geographic Location/Privacy (geopriv), http://datatracker.ietf.org/wg/geopriv/
Beresford, A.R., Stajano, F.: Mix zones: User privacy in location-aware services. In: Proceedings of the Second IEEE Annual Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops, 2004, pp. 127–131. IEEE, Los Alamitos (2004)
Huang, L., Yamane, H., Matsuura, K., Sezaki, K.: Towards modeling wireless location privacy. In: Danezis, G., Martin, D. (eds.) PET 2005. LNCS, vol. 3856, pp. 59–77. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Huang, L., Yamane, H., Matsuura, K., Sezaki, K.: Silent Cascade: Enhancing Location Privacy without Communication Qos Degradation. In: Clark, J.A., Paige, R.F., Polack, F.A.C., Brooke, P.J. (eds.) SPC 2006. LNCS, vol. 3934, pp. 165–180. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Li, M., Sampigethaya, K., Huang, L., Poovendran, R.: Swing & swap: user-centric approaches towards maximizing location privacy. In: Proceedings of the 5th ACM Workshop on Privacy in Electronic Society, pp. 19–28. ACM, New York (2006)
Raya, M., Hubaux, J.P.: The security of vehicular ad hoc networks. In: Proceedings of the 3rd ACM Workshop on Security of Ad Hoc and Sensor Networks, pp. 11–21. ACM, New York (2005)
Gerlach, M., Guttler, F.: Privacy in VANETs using changing pseudonyms-ideal and real. In: IEEE 65th Vehicular Technology Conference, VTC 2007-Spring, pp. 2521–2525. IEEE, Los Alamitos (2007)
Gerlach, M.: Assessing and Improving Privacy in VANETs. ESCAR, Embedded Security in Cars (2006)
Buttyán, L., Holczer, T., Vajda, I.: On the Effectiveness of Changing Pseudonyms to Provide Location Privacy in VANETs. In: Stajano, F., Meadows, C., Capkun, S., Moore, T. (eds.) ESAS 2007. LNCS, vol. 4572, pp. 129–141. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Dötzer, F.: Privacy issues in vehicular ad hoc networks. In: Danezis, G., Martin, D. (eds.) PET 2005. LNCS, vol. 3856, pp. 197–209. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Golle, P., Greene, D., Staddon, J.: Detecting and correcting malicious data in VANETs. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM International Workshop on Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks, pp. 29–37. ACM, New York (2004)
Freudiger, J., Raya, M., Felegyhazi, M., Papadimitratos, P., Hubaux, J.P.: Mix-zones for location privacy in vehicular networks. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Wireless Networking for Intelligent Transportation Systems (WiN-ITS 2007) (2007)
Buttyán, L., Holczer, T., Weimerskirch, A., Whyte, W.: Slow: A practical pseudonym changing scheme for location privacy in vanets. In: 2009 IEEE Vehicular Networking Conference (VNC), pp. 1–8. IEEE, Los Alamitos (2010)
Dahl, M., Delaune, S., Steel, G.: Formal Analysis of Privacy for Vehicular Mix-Zones. In: Gritzalis, D., Preneel, B., Theoharidou, M. (eds.) ESORICS 2010. LNCS, vol. 6345, pp. 55–70. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Poovendran, R., Sampigethaya, K., Huang, L., Li, M., Matsuura, K., Sezaki, K.: CARAVAN: Providing Location Privacy for VANET (2005)
Sampigethaya, K., Li, M., Huang, L., Poovendran, R.: Amoeba: Robust Location Privacy Scheme for Vanet. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 25, 1569–1589 (2007)
Papadimitratos, P., Buttyan, L., Hubaux, J.P., Kargl, F., Kung, A., Raya, M.: Architecture for secure and private vehicular communications. In: 7th International Conference on ITS Telecommunications, ITST 2007, pp. 1–6. IEEE, Los Alamitos (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lim, HJ., Chung, TM. (2011). A Survey on Privacy Problems and Solutions for VANET Based on Network Model. In: Xiang, Y., Cuzzocrea, A., Hobbs, M., Zhou, W. (eds) Algorithms and Architectures for Parallel Processing. ICA3PP 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7017. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24669-2_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24669-2_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-24668-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-24669-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)