Abstract
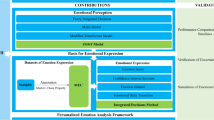
In this paper, we propose a framework to analyze the temporal dynamics of the emotional stimuli. For this framework, both EEG signal and visual information are of great importance. The fusion of visual information with brain signals allows us to capture the users’ emotional state. Thus we adopt previously proposed fuzzy-GIST as emotional feature to summarize the emotional feedback. In order to model the dynamics of the emotional stimuli sequence, we develop a recurrent neuro-fuzzy (RNF) network for modeling the dynamic events of emotional dimensions including valence and arousal. It can incorporate human expertise by IF-THEN fuzzy rule while recurrent connections allow the network fuzzy rules to see its own previous output. The results show that such a framework can interact with human subjects and generate arbitrary emotional sequences after learning the dynamics of an emotional sequence with enough number of samples.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Picard, R.W.: Toward computers that recognize and respond to user emotion. IBM Syst. J. 39(3-4), 705–719 (2000)
Calvo, R., DMello, S.: Affect detection: An interdisciplinary review of models, methods, and their applications. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing 1(1), 18–37 (2010)
Russell, J.A.: A circumplex model of affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 39, 1161–1178 (1980)
Lang, P.J.: The emotion probe. studies of motivation and attention. The American Psychologist 50(5), 372–385 (1995)
Anders, S., Lotze, M., Erb, M., Grodd, W., Birbaumer, N.: Brain activity underlying emotional valence and arousal: a response-related fMRI study. Human Brain Mapping 23(4), 200–209 (2004)
Zhang, Q., Lee, M.: Emotion development system by interacting with human eeg and natural scene understanding. Cognitive Systems Research (in Press, Corrected Proof, 2011)
Oliva, A., Torralba, A.: Building the gist of a scene: the role of global image features in recognition. Progress in Brain Research 155, 22–36 (2006)
Zhang, Q., Lee, M.: Analysis of positive and negative emotions in natural scene using brain activity and gist. Neurocomputing 72(4-6), 1302–1306 (2009)
Burrus, S.C., Burrus, S.C., Gopinath, R.A.: Introduction toWavelets andWavelets Transforms. Prentice-Hall (1997)
Mallat, S.G.: A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 11, 674–693 (1989)
Niemic, C.P.: A theoretical and empirical review of psychophysiological studies of emotion. Journal of Undergraduate Research 1, 15–18 (2002)
Müller, M.M., Keil, A., Gruber, T., Elbert, T.: Processing of affective pictures modulates right-hemispheric gamma band eeg activity. Clinical Neurophysiology 110(11), 1913–1920 (1999)
Kandel, E.R., Schwartz, J.H., Jessell, T.M.: Principles of Neural Science. McGraw- Hill Medical (2000)
Jang, J.S.R., Sun, C.T., Mizutani, E.: Neuro-fuzzy and soft computing: a computational approach to learning and machine intelligence. Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River (1997)
Haykin, S.: Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, Q., Lee, M. (2011). Analyzing the Dynamics of Emotional Scene Sequence Using Recurrent Neuro-Fuzzy Network. In: Lu, BL., Zhang, L., Kwok, J. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7064. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24965-5_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24965-5_38
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-24964-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-24965-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)