Abstract
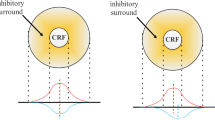
In the real world, the biological visual system is more efficient than the machine visual system in analyzing visual information. Physiology theories show that this efficiency owes to the multi-layer neural network in human visual system, in which every layer accomplishes different tasks and is related with other layers. The low-level stages of the human visual system, especially the retina, can provide certain scale information for the high-level stages of visual system through using the non-classical receptive field (nCRF) mechanism. This mechanism that the nCRF size can be adjusted automatically by ganglion cell (GC) can achieve a multi-scale image analysis. The results, reflecting the distribution of the image information, can be shared by several algorithms or processes solving different visual tasks, such as contour detection and image segmentation. A model of multi-scale image analysis based on GC has been proposed in this paper, which retains the key information and reduces the redundancy information for the further stages of the visual system. Experimental results on N-cut and contour detection show that this multi-scale image analysis model provides distinctive improvement for these image processing tasks.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Portilla, J., Strela, V., Wainwright, M.J., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image denoising using scale mixtures of Gaussians in the wavelet domain. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 12, 1338–1351 (2003)
Guanghong, H., Yingjun, P., Wei, J.: An Improved Image Denoising Method Based on Multi-scale Correlation in Wavelet Domain. In: Conference An Improved Image Denoising Method Based on Multi-scale Correlation in Wavelet Domain (2006)
Mahmoodi, S., Sharif, B.S., Chester, E.G.: Contour detection using multi-scale active shape models. In: Conference Contour Detection using Multi-scale Active Shape Models, vol. 702, pp. 708–711 (1997)
Tremblais, B., Augereau, B.: A fast multi-scale edge detection algorithm. Pattern Recognition Letters 25, 603–618 (2004)
Yang, W., Qianqian, W.: Image segmentation based on multi-scale local feature. In: Conference Image Segmentation Based on Multi-scale Local Feature, pp. 1406–1409 (2010)
Wei, Z., Hongli, D., Dietterich, T.G., Mortensen, E.N.: A Hierarchical Object Recognition System Based on Multi-scale Principal Curvature Regions. In: Conference A Hierarchical Object Recognition System Based on Multi-scale Principal Curvature Regions, pp. 778–782 (2006)
Donoho, D.L., Flesia, A.G.: Can Recent Innovations in Harmonic Analysis Explain Key Findings in Natural Image Statistics? Network: Computation in Neural Systems 12, 371–393 (2001)
Ikeda, H., Wright, M.: The Outer Disinhibitory Surround of the Retinal Ganglion Cell Receptive Field. The Journal of Physiology 226, 511 (1972)
Krüger, J., Fischer, B.: Strong Periphery Effect in Cat Retinal Ganglion Cells. Excitatory Responses in ON- and OFF-center Neurones to Single Grid Displacements. Experimental Brain Research 18, 316–318 (1973)
Chao-Yi, L., Wu, L.: Extensive Integration Field Beyond the Classical Receptive Field of Cat’s Striate Cortical Neurons–Classification and Tuning Properties. Vision Research 34, 2337–2355 (1994)
Chao-Yi, L., Xing, P., Yi-Xiong, Z., Hans-Christoph, M.: Role of the Extensive Area Outside the X-Cell Receptive Field in Brightness Information Transmission. Vision Research 31, 1529–1540 (1991)
Jones, H., Grieve, K., Wang, W., Sillito, A.: Surround Suppression in Primate V1. Journal of Neurophysiology 86, 2011 (2001)
Kapadia, M.K., Westheimer, G., Gilbert, C.D.: Spatial Distribution of Contextual Interactions in Primary Visual Cortex and in Visual Perception. Journal of Neurophysiology 84, 2048 (2000)
Walker, G.A., Ohzawa, I., Freeman, R.D.: Suppression Outside the Classical Cortical Receptive Field. Visual Neuroscience 17, 369–379 (2000)
Grigorescu, C., Petkov, N., Westenberg, M.A.: Contour Detection Based on Nonclassical Receptive Field Inhibition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 12, 729–739 (2003)
Papari, G., Campisi, P., Petkov, N., Neri, A.: IEEE: Contour Detection by Multiresolution Surround Inhibition. In: Proceedings International Conference on Image Processing, vol. 1-7, pp. 749–752 (2006)
Fernandes, B.J.T., Cavalcanti, G.D.C., Ren, T.I.: Nonclassical Receptive Field Inhibition Applied to Image Segmentation. Neural Network World 19, 21–36 (2009)
Zeng, C., Li, Y., Yang, K., Li, C.: Contour Detection Based on a Non-Classical Receptive Field Model with Butterfly-Shaped Inhibition Subregions. Neurocomputing 74, 1527–1534 (2011)
Sivaswamy, G.D.J.J.: Multi-scale Approach to Salient Contour Extraction. In: Conference Multi-scale Approach to Salient Contour Extraction, pp. 186–193 (2005)
Papari, G., Petkov, N.: An Improved Model for Surround Suppression by Steerable Filters and Multilevel Inhibition with Application to Contour Detection. Pattern Recognit. 44, 1999–2007 (2011)
Papari, G., Petkov, N.: Edge and Line Oriented Contour Detection: State of the Art. Image and Vision Computing 29, 79–103 (2011)
Shi, J., Malik, J.: Normalized Cuts and Image Segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 22, 888–905 (2000)
Ghosh, K., Sarkar, S., Bhaumik, K.: Image Enhancement by High-Order Gaussian Derivative Filters Simulating Non-classical Receptive Fields in the Human Visual System. In: Pal, S.K., Bandyopadhyay, S., Biswas, S. (eds.) PReMI 2005. LNCS, vol. 3776, pp. 453–458. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Chaoyi, Q.F.L.: Mathematical Simulation Of Disinhibitory Properties Of Concentric Receptive Field. Acta Biophysica Sinica 11, 214–220 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wei, H., Zuo, Q., Lang, B. (2011). Multi-scale Image Analysis Based on Non-Classical Receptive Field Mechanism. In: Lu, BL., Zhang, L., Kwok, J. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7064. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24965-5_68
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24965-5_68
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-24964-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-24965-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)