Abstract
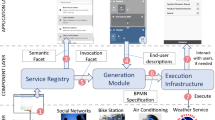
In the Internet of Things, billions of networked and software-driven devices will be connected to the Internet. They can communicate and cooperate with each other to form a composite system. In this paper, we propose PMG-pro (present, model, generate and provide), a language independent, bottom-up and model-driven method for the development of such composite system. We envision that all devices in the Internet of Things provide their functionalities as services. From a service description, a service presenter generates source code (i.e., for the service invocations) and uses an abstract graphical representation to represent a service. The code is connected to the abstract graphical service representation. A service abstractor constructs the abstract graphical representations even more abstract in hierarchical service taxonomy. Software developers use the abstract graphical service presentations to specify new service-based applications, while the source code is used for the automation of code generation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rezafard, A., Vilmos, A., et al.: Internet of things: Strategic research roadmap (2009)
Assmann, U.: Invasive software composition. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Bhattacharjee, A.K., Shyamasundar, R.K.: Validated code generation for activity diagrams. In: Chakraborty, G. (ed.) ICDCIT 2005. LNCS, vol. 3816, pp. 508–521. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Cohen, S.: Ontology and taxonomy of services in a service-oriented architecture. MSDN Libary Infrastructure Architectures 11(11) (2007)
Coyle, L., Neely, S., Stevenson, G., Sullivan, M., Dobson, S., Nixon, P.: Sensor fusion-based middleware for smart homes. International Journal of Assistive Robotics and Mechatronics 8(2), 53–60 (2007)
Zeeb, E., Bobek, A., et al.: WS4D: SOA-Toolkits making embedded systems ready for web services. In: Proceedings of Second International Workshop on Open Source Software and Product Lines. ITEA, Limerick (2007)
Eshuis, R., Wieringa, R.: A formal semantics for uml activity diagrams - formalising workflow models (2001)
Goodwill, J.: Apache Axis Live: A Web Services Tutorial, Sourcebeat (December 2004)
Diaz, G., Pardo, J.-J., Cambronero, M.-E., Valero, V., Cuartero, F.: Automatic translation of ws-cdl choreographies to timed automata. In: Bravetti, M., Kloul, L., Tennenholtz, M. (eds.) EPEW/WS-EM 2005. LNCS, vol. 3670, pp. 230–242. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
IBM. Service component architecture (November 2006), http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/library/specification/ws-sca/
Jeronimo, M., Weast, J.: UPnP Design by Example: A Software Developer’s Guide to Universal Plug and Play. Intel Press, Hillsboro (2003)
Konno, S.: Cyberlink for java programming guide v.1.3 (2005)
Kræmer, F.A.: Arctis and Ramses: Tool suites for rapid service engineering. In: Proceedings of NIK 2007 (Norsk informatikkonferanse). Tapir Akademisk Forlag, Oslo (2007)
Kræmer, F.A.: Engineering Reactive Systems: A Compositional and Model-Driven Method Based on Collaborative Building Blocks. PhD thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim (August 2008)
Grønmo, R., Skogan, D., Solheim, I., Oldevik, J.: Model-Driven web services development. In: Proceedings of International Conference on e-Technology, e-Commerce, and e-Services, pp. 42–45. IEEE Computer Society, USA (2004)
OMG. Model driven architecture guide, version 1.0.1, omg/03-06-01 (June 2003)
OMG. Service oriented architecture modeling language (SoaML): Specification for the UML profile and metamodel for services, UPMS (2009)
Ouyang, C., Verbeek, E., van der Aalst, W.M.P., Breutel, S., Dumas, M., ter Hofstede, A.H.M.: Formal semantics and analysis of control flow in WS-BPEL. Science of Computer Programming 67(2-3), 162–198 (2007)
Papadimitriou, D.: Future internet: The cross-etp vision document. Technical Report Version 1.0, European Future Internet Assembly, FIA (2009)
Quatrani, T.: Visual modeling with Rational Rose 2000 and UML, 2nd edn. Addison-Wesley Longman Ltd., Essex (2000)
Sparx Systems. Enterprise architect, http://www.sparxsystems.com/products/ea/index.html
The SeCSE Team: Designing and deploying service-centric systems: the secse way. In: Proceedings of the Service Oriented Computing: a look at the Inside (SOC @Inside 20 (2007)
Topouzidou, S.: Service oriented development in a unified framework (sodium). Deliverable CD-JRA-1.1.2, SODIUM Consortium (May 2007)
van den Heuvel, W.-J., Zimmermann, O., et al.: Software service engineering: Tenets and challenges. In: Proceedings of the 2009 ICSE Workshop on Principles of Engineering Service Oriented Systems, PESOS 2009, pp. 26–33. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC (2009)
Wu, C.-L., Liao, C.-F., Fu, L.-C.: Service-oriented smart-home architecture based on OSGi and mobile-agent technology. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C: Applications and Reviews, 193–205 (2007)
Su, X., Svendsen, R., et al.: Description of the ISIS Ecosystem Towards an Integrated Solution to Internet of Things. Telenor Group Corporate Development (2010)
Yermashov, K.: Software Composition with Templates. PhD Thesis, De Montfort University, UK (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sulistyo, S., Prinz, A. (2011). PMG-Pro: A Model-Driven Development Method of Service-Based Applications. In: Ober, I., Ober, I. (eds) SDL 2011: Integrating System and Software Modeling. SDL 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7083. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25264-8_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25264-8_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-25263-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-25264-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)