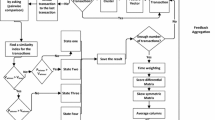
Abstract
With the growth of e-commerce, online reputation system has become the important character in many e-commerce sites. The trust between seller and customer established relying on the reputation system. This make the fairness and accuracy of reputation computing model are very important. Current, most reputation computing models cannot reach the objectives, because they didn’t consider the number of objects’ ratings. In this paper, we propose a novel computing model which use one-way random effects model. This model introduces the random effects, and considers the number of objects’ ratings. the random effects is predicted by BLUP(Best linear unbiased Prediction).We have evaluated the difference of top k lists by this model from that by average model in real data sets, and proof the fairness and accuracy of this model using cases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Houser, D., Wooders, J.: Reputation in auctions: theory and evidence from eBay. Journal of Economics and Management Strategy 15(2), 353–369 (2006)
Resnick, P., Zeckhauser, R., Friedman, E., Kuwabara, K.: Reputation systems. Communications of the ACM 43(12), 45–48 (2000)
Fouss, F., Achbany, Y., Saerens, M.: A probabilistic reputation model based on transaction ratings. Information Sciences 180, 2095–2123 (2010)
Resnick, P., Zeckhauser, R.: Trust among Strangers in Internet Transactions: Empirical Analysis of eBay’s Reputation System. The Economics of the Internet and E-Commerce 11, 127–157 (2002)
Bharadwaj, K.K., Al-Shamri, M.Y.H.: Fuzzy computation models for trust and reputation. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications 8, 37–47 (2009)
Jøsang, A., Ismail, R., Boyd, C.: A survey of trust and reputation systems for online service provision. Decision Support Systems 43(2), 618–644 (2007)
Dellarocas, C.: Immunizing online reputation reporting systems against unfair ratings and discriminatory behavior. In: Proceedings of the 2nd ACM Conference on Electronic Commerce, pp. 150–157. ACM Press, New York (2000)
Fan, M., Whinston, A.B.: Evaluation and design of online cooperative feedback mechanisms for reputation management. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 17(2), 244–254 (2005)
Withby, A., Josang, A., Indulska, J.: Filtering out unfair ratings in Bayesian reputation systems. The Icfain Journal of Management Research 4(2), 48–64 (2005)
Peixoto, J.L., Harville, D.A.: Comparison of Alternative Predictors Under the Balanced One-Way Random Model. Journal of the American Association Association 81(394), 431–436 (1986)
Donner, A.: A Review of Inference procedures for the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient in the One-way Random Effects Model. International Statistical Review 54(1), 67–82 (1986)
Robinson, G.K.: That BLUP is a Good Thing: The Estimation of Random Effects. Statistical Science 6(1), 15–32 (1991)
Dwork, C., Kumar, R., Naor, M., Sivakumar, D.: Rank Aggregation Methods for the Web. In: Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 613–622. ACM Press, Hong Kong (2001)
Fagin, R., Kumar, R., Sivakumar, D.: Comparing Top K Lists. SIAM J. Discrete Mathematics 17(1), 134–160 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, Y., Li, Q., Lin, Z. (2011). A Novel Reputation Computing Model. In: Chen, L., Yung, M. (eds) Trusted Systems. INTRUST 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6802. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25283-9_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25283-9_21
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-25282-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-25283-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)