Abstract
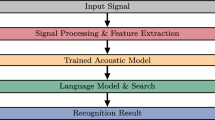
Incorrect recognition of adjacent small words is considered one of the obstacles in improving the performance of automatic continuous speech recognition systems. The pronunciation variation in the phonemes of adjacent words introduces ambiguity to the triphone of the acoustic model and adds more confusion to the speech recognition decoder. However, small words are more likely to be affected by this ambiguity than longer words. In this paper, we present a data-driven approach to model the small words problem. The proposed method identifies the adjacent small words in the corpus transcription to generate the compound words. The unique compound words are then added to the expanded pronunciation dictionary, as well as to the language model as a new sentence. Results show a significant improvement of 2.16% in the word error rate compared to that of the Baseline speech corpus of Modern Standard Arabic broadcast news.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tajchman, G., Fosler, E., Jurafsky, D.: Building multiple pronunciation models for novel words using exploratory computational phonology. In: EUROSPEECH 1995, Madrid, Spain, pp. 2247–2250 (1995)
Finke, M., Waibel, A.: Speaking mode dependent pronunciation modeling in large vocabulary conversational speech recognition. In: Proc. of EuroSpeech 1997, Rhodes, pp. 2379–2382 (1997)
Beulen, K., Ortmanns, S., Eiden, A., Martin, S., Welling, L., Overmann, J., Ney, H.: Pronunciation modelling in the RWTH large vocabulary speech recognizer. In: Proc. of the ESCA Workshop Modeling Pronunciation Variation for Automatic Speech Recognition, pp. 13–16 (1998)
Fosler-Lussier, E., Greenberg, S., Morgan, N.: Incorporating Contextual Phonetics into Automatic Speech Recognition. In: International Congress of Phonetic Sciences (ICPhS 1999), San Francisco, California, pp. 611–614 (1999)
Saon, G., Padmanabhan, M.: Data-driven approach to designing compound words for continuous speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing 9(4), 327–332 (2001), doi:10.1109/89.917678
Elshafei Ahmed, M.: Toward an Arabic Text-to-Speech System. The Arabian Journal of Science and Engineering 16(4B), 565–583 (1991)
Alghamdi, M., Almuhtasib, H., Elshafei, M.: Arabic Phonological Rules. King Saud University Journal: Computer Sciences and Information 16, 1–25 (2004)
Elshafei, M., Almuhtasib, H., Alghamdi, M.: Techniques for High Quality Text-to-speech. Information Science 140(3-4), 255–267 (2002)
Ali, M., Elshafei, M., Al-Ghamdi, M., Al-Muhtaseb, H., Al Najjar, A.: Generation of Arabic phonetic dictionaries for speech recognition. In: 5th International Conference on Innovations in Information Technology, United Arab Emirates (December 2008)
Plötz, T.: Advanced stochastic protein sequence analysis, Ph.D. Thesis, Bielefeld University (June 2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
AbuZeina, D., Al-khatib, W., Elshafei, M. (2011). Small-Word Pronunciation Modeling for Arabic Speech Recognition: A Data-Driven Approach. In: Salem, M.V.M., Shaalan, K., Oroumchian, F., Shakery, A., Khelalfa, H. (eds) Information Retrieval Technology. AIRS 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7097. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25631-8_48
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25631-8_48
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-25630-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-25631-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)