Abstract
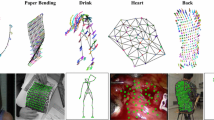
We introduce a non-linear stochastic filtering technique to track the state of a free curve from image data. The approach we propose is implemented through a particle filter, which includes color measurements characterizing the target and the background respectively. We design a continuous-time dynamics that allows us to infer inter-frame deformations. The curve is defined by an implicit level-set representation and the stochastic dynamics is expressed on the level-set function. It takes the form of a stochastic partial differential equation with a Brownian motion of low dimension. Specific noise models lead to the traditional level set evolution law based on mean curvature motions, while other forms lead to new evolution laws with different smoothing behaviors. In these evolution models, we propose to combine local photometric information, some velocity induced by the curve displacement and an uncertainty modeling of the dynamics. The associated filter capabilities are demonstrated on various sequences with highly deformable objects.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnaud, E., Mémin, E.: Partial linear gaussian model for tracking in image sequences using sequential monte carlo methods. IJCV 74(1), 75–102 (2007)
Chan, T., Vese, L.: An active contour model without edges. In: Scale-Space Theories in Computer Vision, pp. 141–151 (1999)
Cremers, D., Soatto, S.: Motion competition: A variational framework for piecewise parametric motion segmentation. IJCV 62(3), 249–265 (2005)
Crisan, D., Doucet, A.: A survey of convergence results on particle filtering methods for practitioners. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 50(3), 736–746 (2002)
Dambreville, S., Rathi, Y., Tannenbaum, A.: Tracking deformable objects with unscented kalman filtering and geometric active contours. In: American Control Conference, pp. 1–6 (2006)
Feil, B., Kucherenko, S., Shah, N.: Comparison of monte carlo and quasi monte carlo sampling methods in high dimensional model representation. In: Proceedings of the 2009 First International Conference on Advances in System Simulation, pp. 12–17. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, USA (2009)
Goldenberg, R., Kimmel, R., Rivlin, E., Rudzsky, M.: Fast geodesic active contours. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 10(10), 1467–1475 (2001)
Kimmel, R., Bruckstein, A.M.: Tracking level sets by level sets: a method for solving the shape from shading problem. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. (1995)
Niethammer, M., Tannenbaum, A.: Dynamic geodesic snakes for visual tracking. In: CVPR (1), pp. 660–667 (2004)
Nummiaro, K., Koller-Meier, E., Gool, L.V.: An adaptive color-based particle filter. Image and Vision Computing 21(1), 99–110 (2003)
Osher, S., Sethian, J.A.: Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: Algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. Journal of Computational Physics 79, 12–49 (1988)
Paragios, N., Deriche, R.: Geodesic active regions: a new framework to deal with frame partition problems in computer vision. J. of Visual Communication and Image Representation 13, 249–268 (2002)
Pons, J.P., Hermosillo, G., Keriven, R., Faugeras, O.: Maintaining the point correspondence in the level set framework. Journal of Computational Physics 220(1), 339–354 (2006)
Rathi, Y., Vaswani, N., Tannenbaum, A., Yezzi, A.: Tracking deforming objects using particle filtering for geometric active contours. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 29(8), 1470–1475 (2007)
Sethian, J.A.: Theory, algorithms, and applications of level set methods for propagating interfaces. Acta Numerica 5(-1), 309–395 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Avenel, C., Mémin, E., Pérez, P. (2012). Tracking Level Set Representation Driven by a Stochastic Dynamics. In: Boissonnat, JD., et al. Curves and Surfaces. Curves and Surfaces 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6920. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27413-8_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27413-8_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-27412-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-27413-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)