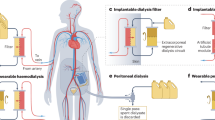
Abstract
In a given treatment modality, the performance characteristics of the dialyzer determine the quantity and nature of uremic toxins removed from the patient’s blood, provided that an adequate treatment time and flow conditions are prescribed. Dialyzer selection may be the most difficult task facing a dialysis facility. Practitioners must understand the functions of a dialyzer, membrane biocompatibility, implications of poor technique, financial and quality implications of dialyzer reprocessing, and matching the patient to the dialyzer’s capabilities. Dialyzer membranes are a vital contributor to the success or failure of hemodialysis therapies and hemodialysis adequacy. Matching a dialyzer to patient requirements is crucial to meet the prescribed clearance goals.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akizawa, T., Kinugasa, E., Ideura, T.: Classification of dialysismem-branes by performance. Contrib. Nephrol. 113, 25–31 (1995)
Ambalavanan, S., Rabetoy, G., Cheung, A.: High efficiency and high flux hemodialysis. In: Schrier, R.W. (ed.) Atlas of Diseases of the Kidney. Current Medicine, vol. 5, pp. 3.1–3.10, Philadelphia (1999)
Ayli, M., Ayli, D., Azak, A., et al.: The effect of high-flux hemodialysis on dialysis-associated amyloidosis. Ren. Fail. 27(1), 31–34 (2005)
Bagnasco, S.M.: The erythrocyte urea transporter UT-B. J. Membr. Biol. 212(2), 133–138 (2006)
Bhimani, J.P., Ouseph, R., Ward, R.A.: Effect of increasing dialysate flow rate on diffusive mass transfer of urea, phosphate and beta2-microglobulin during clinical haemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 25(12), 3990–3995 (2010)
Collins, A.J., Keshaviah, P.: High-efficiency, high flux therapies in clinical dialysis. In: Nissenson, A.R. (ed.) Clinical Dialysis, 3rd edn., pp. 848–863 (1995)
Collins, A.J.: High-flux, high-efficiency procedures. In: Henrich, W. (ed.) Principles and Practice of Hemodialysis, pp. 76–88. Appleton & Large, Norwalk (1996)
Choong, L., Leypoldt, J.K., Cheung, A.: Dialyzer mass transfer-area co-efficients during clinical hemodialysis are dependent on both blood flow and dialysate flow rates (abstract). J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 10, 189A (1999)
Cheung, A.K., Levin, N.W., Greene, T., et al.: Effects of high-flux hemo-dialysis on clinical outcomes: results of the HEMO study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 14(12), 3251–3263 (2003)
Cheung, A.K., Leypoldt, J.K.: The hemodialysis membranes: a historical perspective, current state and future prospect. Semin. Nephrol. 17(3), 196–213 (1997)
Clark, W.R., Hamburger, R.H., Lysaght, M.J.: Effect of membrane composition and structure on solute removal and biocompatibility in hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 56(6), 2005–2015 (1999)
Clark, W.R., Shinaberger, J.H.: Effect of Dialysateside Mass Transfer Resistance on Small Solute Removal in Hemodialysis. Blood Purif. 18(4), 260–263 (2000)
Curtis, J.: Splitting fibers: understanding how dialyzer differences can impact adequacy. Nephrol. News Issues 5(6), 36–39 (2001)
Daniels, I.D., Berlyne, G.M., Barth, R.H.: Blood flow rate and access recirculation in hemodialysis. Int. J. Artif. Organs 15(8), 470–474 (1992)
Daugirdas, J.T., Blake, P.G., Ing, T.S.: Handbook of Dialysis, 4th edn. Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia (2007)
Daugirdas, J.T., Depner, T.A.: A nomogram approach to hemodialysis urea modeling. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 23(1), 33–40 (1994)
Depner, T.A., Greene, T., Daugirdas, J.T., et al.: Dialyzer performance in the HEMO study: in vivo KoA and true blood flow determined from a model of cross-dialyzer urea extraction. ASAIO J. 50(1), 85–93 (2004)
Gotch, F.A., Panlilio, F., Sergeyeva, O., et al.: Effective diffusion volume flow rates (Qe) for urea, creatinine, and inorganic phosphorous (Qeu, Qecr, QeiP) during hemodialysis. Semin. Dial. 16(6), 474–476 (2003)
Granger, A., Vantard, G., Vantelon, J., Perrone, B.: A mathematical ap-proach of simultaneous dialysis and filtration (SDF). In: Proc. Eur. Soc. Artif. Organs, vol. 5, pp. 174–177 (1978)
Hauk, M., Kuhlmann, M.K., Riegel, W., et al.: In vivo effects of dialys-ate flow rate on Kt/V in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 35(1), 105–111 (2000)
Hamilton, R.W.: Principles of Dialysis: Diffusion, Convection, and Dialysis Machines. In: Schrier, R.W. (ed.) Atlas of Diseases of the Kidney. Current Medicine, vol. 5, pp. 1.1–1.6. Blackwell Science, Philadelphia (1998)
Henderson, L.W.: Biophysics of Ultrafiltration and Hemofiltration in Replacement of renal function by dialysis. In: Jacobs, C., Kjellstrand, C.M., Koch, K.M., Winchester, J.F. (eds.), pp. 114–145. Kluwer Aca-demic Publisher (1996)
Hoenich, N.A., Ronco, C.: Selecting a Dialyzer: Technical and Clinical Considerations. In: Nissenson, A.R., Fine, R.N. (eds.) Handbook of Dialysis Therapy, 4th edn., pp. 263–278. Hanley &Belfus, Inc., Philadelphia (2008)
Jaffrin, M.Y.: Convective mass transfer in hemodialysis. Artif. Organs 19(11), 1162–1171 (1995)
Keshaviah, P., Luehmann, D., Ilstrup, K., Collins, A.: Technical requirements for rapid high efficiency therapies. Artif. Organs 10(3), 189–194 (1986)
Khandpur, R.S.: Handbook of Biomedical Instrumentation, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill Professional (2003)
Klinkmann, H., Vienken, J.: Membranes for dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 10(suppl. 3), 39–45 (1995)
Klinkmann, H., Ebbinghausen, H., Uhlenbusch, I., Vienken, J.: High flux dialysis, dialysate quality and backtransport. In: Bonomini, V. (ed.) Evolution in Dialysis Adequacy. Contr. Nephrol., vol. 103, pp. 89–97 (1993)
Korwer, U., Schorn, E.B., Grassmann, A., Vienken, J.: Understanding Membranes and Dialyzers. PABST Science Publishers (2004)
Leypoldt, J.K., Cheung, A.K., Chirananthavat, T., et al.: Hollow fiber shape alters solute clearances in high flux hemodialyzers. ASAIO J. 49(1), 81–87 (2003)
Leypoldt, J.K.: Solute fluxes in different treatment modalities. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 15(suppl. 1), 3–9 (2000)
Leypoldt, J.K., Cheung, A.: Effect of low dialysate flow rates on hemodialyzer mass transfer area coefficients for urea and creatinine. Home HD Int. 3, 51–54 (1999)
Leypoldt, J.K., Cheung, A.K., Agodoa, L.Y., et al.: Hemodialyzer mass transfer-area coefficients for urea increase at high dialysate flow rates. Kidney Int. 51(6), 2013–2017 (1997)
Leypoldt, J.K.: Effect of Increasing Dialysate Flow Rate on KoA and Dialyzer Urea Clearance. Semin. Dial. 11(3), 195–196 (1998)
Lim, V.S., Flanigan, M.J., Fangman, J.: Effect of hematocrit on solute removal during high efficiency hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 37(6), 1557–1559 (1990)
Locatelli, F., Valderrabano, F., Hoenich, N., et al.: Progress in dialysis technology: membrane selection and patient outcome. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 15(8), 1133–1139 (2000)
Lonnemann, G., Sereni, L., Lemke, H.D., Tetta, C.: Pyrogen retention by highly permeable synthetic membranes during in vitro dialysis. Artif. Organs 25(12), 951–960 (2001)
MacLeod, A., Daly, C., Khan, I., et al.: Comparison of cellulose, modi-fied cellulose and synthetic membranes in the haemodialysis of patients with end-stage renal disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 3:CD003234 (2001)
Mandolfo, S., Malberti, F., Imbasciati, E., Cogliati, P., Gauly, A.: Impact of blood and dialysate flow and surface on performance of new polysulfone hemodialysis dialyzers. Int. J. Artif. Organs 26(2), 113–120 (2003)
Michaels, A.S.: Operating parameters and performance criteria for hemodialyzers and other membrane-separation devices. Trans. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 12, 387–392 (1966)
Ofsthun, N.J., Zydney, A.L.: Importance of convection in artificial kid-ney treatment. In: Maeda, K., Shinzato, T. (eds.) Effective Hemodiafiltration: New Methods, pp. 54–70. Karger Publisher, Basel (1994)
Ofsthun, N.J., Leypoldt, J.K.: Ultrafiltration and backfiltration during hemodialysis. Artif. Organs 19(11), 1143–1161 (1995)
Okada, M., Takesawa, S., Watanabe, T., et al.: Effects of zeta potential on the permeability of dialysis membranes to inorganic phosphate. ASAIO Trans. 35(3), 320–322 (1989)
Ouseph, R., Ward, R.A.: Increasing dialysate flow rate increases dialyzer urea mass transfer-area coefficients during clinical use. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 37(2), 316–320 (2001)
Palmer, B.F.: The Dialysis Prescription and Urea Modeling. In: Schrier, R.W. (ed.) Atlas of Diseases of the Kidney, Current Medicine, vol. 5, pp. 6.1–6.8. Blackwell Science, Philadelphia (1998)
Ronco, C., Brendolan, A., Crepaldi, C., et al.: Blood and dialysate flow distributions in hollow fiber hemodialyzers analyzed by computerized helical scanning technique. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 13, S53–S61 (2002)
Ronco, C., Ghezzi, P.M., Metry, G., et al.: Effects of hematocrit and blood flow distribution on solute clearance in hollow fiber hemodialyzers. Nephron 89(3), 243–250 (2001)
Ronco, C., Heifetz, A., Fox, K., et al.: Beta 2-microglobulin removal by synthetic dialysis membranes. Mechanisms and kinetics of the molecule. Int. J. Artif. Organs 20, 136–143 (1997)
Ronco, C.: Backfiltration in clinical dialysis: nature of the phenomenon, mechanisms and possible solutions. Int. J. Artif. Organs 13, 11–21 (1990)
Sargent, J.A., Gotch, F.A.: Principles and biophysics of dialysis in Re-placement of renal function by dialysis. In: Jacob, C., Kjellstrand, C.M., Koch, K.M., Winchester, J.F. (eds.), 4th edn., pp. 188–230. Kluwer Academic Publiher, Dordrecht (1996)
Waniewski, J., Werynski, A., Ahrenholz, P., et al.: Theoretical basis and experimental verification of the impact of ultrafiltration on dialyzer clearance. Artif. Organs 15(2), 70–77 (1991)
Werynski, A.: Evaluation of the impact of ultrafiltration on dialyzer clearance. Artif. Organs 3(2), 140–142 (1979)
Woods, H.F., Nandakumar, M.: Improved outcome for haemodialysis patients treated with high-flux membranes. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 15, 36–42 (2000)
Yamamoto, K., Matsukawa, H., Yakushiji, T., et al.: Technical evaluation of dialysate flow in a newly designed dialyzer. ASAIO J. 53(1), 36–40, 14 (2007)
Yamamoto, K., Matsuda, M., Hirano, A., et al.: Computational evaluation of dialysis fluid flow in dialyzers with variously designed jackets. Artif. Organs 33(6), 481–486 (2009)
Zucchelli, P., Santoro, A.: Inorganic phosphate removal during different dialytic procedures. Int. J. Artif. Organs 10(3), 173–178 (1987)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Azar, A.T. (2013). Dialyzer Performance Parameters. In: Azar, A. (eds) Modelling and Control of Dialysis Systems. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 404. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27458-9_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27458-9_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-27457-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-27458-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)