Abstract
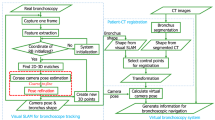
We present a novel approach to motion compensation for bronchoscope navigation where the bronchoscope trajectory is modeled using a spline curve. Initial position and orientation measurements from electromagnetic tracking are refined using the distance of the trajectory from airways segmented in preoperative CT data, and similarity between real and virtual bronchoscopic images. We present an evaluation on a dynamic motion phantom and on a moving ex-vivo porcine lung. Ground truth data is provided by human experts.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mori K, Deguchi D, Akiyama K, et al. Hybrid bronchoscope tracking using a magnetic tracking sensor and image registration. Proc MICCAI. 2005; p. 543–50.
Gergel I, dos Santos TR, Tetzlaff R, et al. Particle filtering for respiratory motion compensation during navigated bronchoscopy. Proc SPIE. 2010; p. 76250W.
Luo X, Kitasaka T, Mori K. Bronchoscopy navigation beyond electromagnetic tracking systems: a novel bronchoscope tracking prototype. Proc MICCAI. 2011; p. 194–202.
Reichl T, andManuela Menzel IG, Hautmann H, et al. Real-time motion compensation for EM bronchoscope tracking with smooth output: ex-vivo validation. Proc SPIE. 2012.
Soper TD, Haynor DR, Glenny RW, et al. In vivo validation of a hybrid tracking system for navigation of an ultrathin bronchoscope within peripheral airways. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2010;57:736–45.
Catmull E, Rom R. A class of interpolating splines. Computer Aided Geometric Design. 1974; p. 317–26.
Shoemake K. Animating rotation with quaternion curves. Proc SIGGRAPH. 1985.
Reichl T, Luo X, Menzel M, et al. Deformable registration of bronchoscopic video sequences to CT volumes with guaranteed smooth output. Proc MICCAI. 2011; p. 17–24.
Wengert C, Reeff M, Cattin P, et al. Fully automatic endoscope calibration for intraoperative use. Proc BVM. 2006; p. 419–23.
Solomon SB, White Jr P, Wiener CM, et al. Three-dimensional CT-guided bron- choscopy with a real-time electromagnetic position sensor: a comparison of two image registration methods. Chest. 2000;118:1783–7.
Luo X, Feuerstein M, Sugiura T, et al. Towards hybrid bronchoscope tracking under respiratory motion: evaluation on a dynamic motion phantom. Proc SPIE. 2010; p. 76251B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Reichl, T. et al. (2012). Motion Compensation for Bronchoscope Navigation Using Electromagnetic Tracking, Airway Segmentation, and Image Similarity. In: Tolxdorff, T., Deserno, T., Handels, H., Meinzer, HP. (eds) Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2012. Informatik aktuell. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-28502-8_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-28502-8_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-28501-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-28502-8
eBook Packages: Computer Science and Engineering (German Language)