Abstract
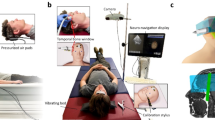
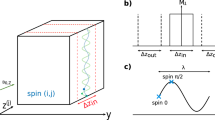
Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is capable of “palpating” the brain by measuring externally induced intracranial shear waves with high spatial and temporal resolution. Conventional MRE is limited as it either relies on two-dimensional multifrequency wave acquisition or three-dimensional vector field MRE at single frequencies. However, full assessment of spatially resolved viscoelastic constants requires both, the acquisition of full shear wave fields and broad dynamic range MRE at multiple frequencies. We therefore propose fast single-shot MRE at 3 Tesla magnetic field strength combined with continuous wave stimulation and interleaved image slice acquisition. By this protocol, a full three dimensional MRE data set is acquired within 60, which may readily be repeated for multifrequency data acquisition. The feasibility of the method is demonstrated in the brain of one healthy volunteer at 50Hz mechanical excitation frequency. The measured complex modulus values are in agreement with results reported in the literature.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muthupillai R, Lomas D, Rossman P, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography by direct visualization of propagating acoustic strain waves. Science. 1995;269(5232):1854–7.
Sack I, Beierbach B, Wuerfel J, et al. The impact of aging and gender on brain viscoelasticity. Neuroimage. 2009;46(3):652–7.
Wuerfel J, Paul F, Beierbach B, et al. MR-elastography reveals degradation of tissue integrity in multiple sclerosis. Neuroimage. 2010;49(3):2520–5.
Murphy MC, Huston J, Jack CR, et al. Decreased brain stiffness in Alzheimer’s disease determined by magnetic resonance elastography. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;34(3):494–8.
Oliphant TE, Manduca A, Ehman RL, et al. Complex-valued stiffness reconstruction for magnetic resonance elastography by algebraic inversion of the differential equation. Magn Reson Med. 2001;45(2):299–310.
Rump J, Klatt D, Braun J, et al. Fractional encoding of harmonic motions in MR elastography. Magn Reson Med. 2007;57(2):388–95.
Green MA, Bilston LE, Sinkus R. In vivo brain viscoelastic properties measured by magnetic resonance elastography. NMR Biomed. 2008;21(7):755–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Fehlner, A., Hirsch, S., Braun, J., Sack, I. (2012). Fast 3D Vector Field Multi-Frequency Magnetic Resonance Elastography of the Human Brain. In: Tolxdorff, T., Deserno, T., Handels, H., Meinzer, HP. (eds) Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2012. Informatik aktuell. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-28502-8_63
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-28502-8_63
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-28501-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-28502-8
eBook Packages: Computer Science and Engineering (German Language)