Abstract
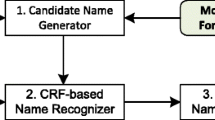
Recognition of chinese personal names becomes a difficult and key point in chinese unknown word recognition. This paper explored the context boundary of names and the law of names. The context boundary of names is concentrated, which can reduce recognition errors brought up by Forward Maximum Matching Segmentation; from real text corpus, we discover that names begin with surname, dislocation characters of names reach 70.83%, and rare characters of names reach 9.42%. This paper improved the Forward Maximum Matching Segmentation and implemented a name recognition test based on CRFs, which was combined with the surname, the context boundary, the dislocation character and the rare character. The open test shows that recall reaches 91.24% from BakeOff-2005.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, H., Liu, Q.: Automatic Recognition of Chinese Person Name Based on Role Tagging. Chinese Journal of Computers 27(1), 86–91 (2004)
CRFs++0.53[OL].[2009], http://sourceforge.net/projects/crfpp/
Zhou, G., Su, J.: Named Entity Recognition using an HMM-based Chunk Tagger. In: Proc. of the 40th Annual Meeting of the ACL, Philadelphia, pp. 473–480 (2002)
Oliver, B., Josef, O.F., Hermann, N.: Maximum Entropy Models for Named Entity Recognition. In: Proc. of the Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning, Edmonton, Canada, pp. 148–151 (2003)
Zhang, Y., Xu, B., Cao, Y., Zong, C.: Research of Chinese Person Names Identification Based on Surname. Computer Engineering and Applications (4), 62–65 (2003)
Lafferty, J., McCallum, A., Pereira, F.: Conditional Random Fields Probabilistic Models for Segmenting and Labeling Sequence Data. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (2001)
Xiang, X.: Chinese Named Entity Recognition based on Conditional Random Fields. Xiamen University (2006)
Xue, N.: Chinese word segmentation as character tagging. Computational Linguistics and Chinese Language Processing 8(1), 29–48 (2003)
Liang, N.: CDWS the Mordern Printed Chinese Distinguishing Word System. Journal of Chinese Information Processing 1(2), 44–52 (1987)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lvexing, Z., Xueqiang, L., Kun, L., Yuncheng, D. (2012). Recognition of Chinese Personal Names Based on CRFs and Law of Names. In: Wang, H., et al. Web Technologies and Applications. APWeb 2012. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7234. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-29426-6_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-29426-6_20
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-29425-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-29426-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)