Abstract
Web service composition refers to the creation process of a composite service which offers a new functionality, from existed web services, in order to reach a determined goal in a user request. In many real-life Web service composition scenarios, on the other hand, the aim is to generate a solution that not only achieves some goals and any constraints associated with them, but also is desirable with respect to some user preferences and its contextual characteristics. Therefore, a solution composition must satisfy those preferences as much as possible.
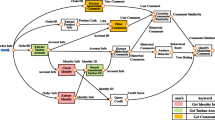
In this paper, we first propose a model, named Profile, which describes in the same time user and service context. We propose also, a system of composition plan generation which uses the user needs expressed in a request. The taking into account of the user preferences and contextual information is realized, in our solution, by the use of a similarity measure between user and web services profiles along the composition process (web services discovery and composition plan generation).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aït-Bachir, A.: Measuring similarity of service interfaces. In: Proc. of the PhD Symposium at ICSOC 2008. CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol. 421 (2008)
Dietze, S., Gugliotta, A., Domingue, J.: Exploiting Metrics for Similarity-based Semantic Web Service Discovery. In: IEEE 7th International Conference on Web Services (ICWS 2009), Los Angeles, CA, USA (2009)
Wu, Z., Ranabahu, A., Gomadam, K., Sheth, A.P., Miller, J.A.: Automatic Composition of Semantic Web Services using Process Mediation. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2007), Funchal, Portugal, pp. 453–461 (June 2007)
Lopez-Velasco, C.: AWSDL: A WSDL Extension for Adapted Web Services. In: Actes 23th Congress INFORSID, pp. 133–148 (2005) (in French)
Albers, P., Licchelli, O.: Personalized Web Service Composition. In: Intelligence Artificielle et Web Intelligence, Grenoble (2007) (in French)
Bouyakoub, F.M., Belkhir, A.: AdaMS: an adaptation multimedia system for heterogeneous environments. In: Second IFIP Int. Conf. on New Technologies, Mobility and Security, NTMS 2008, Tangier, Morocco, pp. 42–46 (2008)
Lemlouma, T.: Negotiation and Adaptation Architecture of Multimedia Services in Heterogeneous Environment. PHD Thesis, Polytechnic National Institut of Grenoble (2004) (in French)
Fouial, O.: Discovery and Supply Adaptative Services in Mobile Environments. Thesis, Superior National School of Telecommunication (ENST), Computer and Networks Department (2004) (in French)
Klyn, G., Reynolds, F., Woodrow, C., Ohto, H., Hjelm, J., Butler, M.H., Tran, L.: Composite Capability/Preference Profile (CC/PP): Structure and Vocabularies 1.0, W3C Recommendation (2004)
Lin, D.: An Information-Theoretic Definition of similarity. In: Proceedings of the Fifteenth International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 1998). Morgan- Kaufmann, Madison (1998)
Belkhirat, A., Belkhir, A., Bouras, A.: A New Similarity Measure for the Profiles Management. In: 2011 UkSim 13th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation (UKSim), Cambridge, United Kingdom, pp. 255–259 (2011), doi:10.1109/UKSIM.2011.55
Batageli, V., Bern, M.: Comparing measures. Extension of paper represented at DISTANCIA 1992, Rennes, France (1992)
Bouyakoub, F.M., Belkhir, A.: A similarity measure for the negotiation in web services. Springer Science + Business Media, LLC (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Atika, O., Abedelkader, B. (2012). Composing Web Services Using Profiles Similarity. In: Benlamri, R. (eds) Networked Digital Technologies. NDT 2012. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 294. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-30567-2_43
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-30567-2_43
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-30566-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-30567-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)