Abstract
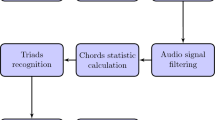
We have developed a method that identifies musical chords in polyphonic musical signals. As musical chords mainly represent the harmony of music and are related to other musical elements such as melody and rhythm, we should be able to recognize chords more effectively if this interrelationship is taken into consideration. We use bass pitches as clues for improving chord recognition. The proposed chord recognition system is constructed based on Viterbi-algorithm-based maximum a posteriori estimation that uses a posterior probability based on chord features, chord transition patterns, and bass pitch distributions. Experimental results with 150 Beatles songs that has keys and no modulation showed that the recognition rate was 73.7% on average.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sheh, A., Ellis, D.P.: Chord segmentation and recognition using EM-trained hidden Markov models. In: ISMIR 2003, pp. 183–189 (2003)
Bello, J.P., Pickens, J.: A robust mid-level representation for harmonic content in music signals. In: ISMIR 2005, pp. 304–311 (2005)
Lee, K., Slaney, M.: A unified system for chord transcription and key extraction using hidden Markov models. In: ISMIR 2007, 245–250 (2007)
Fujishima, T.: Realtime chord recognition of musical sound: A system using common lisp music. In: ICMC 1999, pp. 464–467 (1999)
Harte, C., Sandler, M., Gasser, M.: Detecting harmonic change in musical audio. In: AMCMM 2006, pp. 21–26 (2006)
Yoshioka, T., Kitahara, T., Komatani, K., Ogata, T., Okuno, H.G.: Automatic chord transcription with concurrent recognition of chord symbols and boundaries. In: ISMIR 2004, pp. 100–105 (2004)
Sumi, K., Itoyama, K., Yoshii, K., Komatani, K., Ogata, T., Okuno, H.G.: Automatic chord recognition based on probabilistic integration of chord transition and bass pitch estimation. In: ISMIR 2008, pp. 39–44 (2008)
Mauch, M., Dixon, S.: Simultaneous estimation of chords and musical context from audio. IEEE Trans. Audio, Speech and Lang. Process. 18, 1280–1289 (2010)
Teh, Y.W.: A hierarchical bayesian language model based on Pitman-Yor processes. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Computational Linguistics and the 44th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (COLING-ACL 2006), ACL-44, pp. 985–992. Association for Computational Linguistics, Stroudsburg (2006)
Goto, M.: An audio-based real-time beat tracking system for music with or without drum-sounds. J. New Music Res. 30, 159–171 (2001)
Goto, M.: A chorus-section detecting method for musical audio signals. In: ICASSP 2003, pp. V–437–V–440 (2003)
Goto, M.: A real-time music-scene-analysis system: Predominant-F0 estimation for detecting melody and bass lines in real-world audio signals. Speech Communication 43, 311–329 (2004)
Harte, C., Sandler, M., Abdallah, S., Gómez, E.: Symbolic representation of musical chords: A proposed syntax for text annotations. In: ISMIR 2005, pp. 66–71 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Itoyama, K., Ogata, T., Okuno, H.G. (2012). Automatic Chord Recognition Based on Probabilistic Integration of Acoustic Features, Bass Sounds, and Chord Transition. In: Jiang, H., Ding, W., Ali, M., Wu, X. (eds) Advanced Research in Applied Artificial Intelligence. IEA/AIE 2012. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 7345. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31087-4_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31087-4_7
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-31086-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-31087-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)