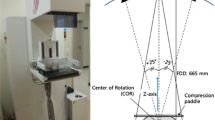
Abstract
There are two basic tomosynthesis data acquisition modes: step-and-shoot. Most experimental research on tomosynthesis has been done using commercial breast tomosynthesis systems, which can operate in only a single mode, either step-and-shoot or continuous motion. Thus the only studies that have been done to compare these two imaging modes for otherwise identical systems have been simulation studies. In this paper we describe a versatile, bench-top 3D breast imaging system that can acquire tomosynthesis data using either mode. Preliminary experimental studies of in-plane blur and artifact propagation using different acquisition protocols are discussed. Our initial results indicate that, noticeable difference was observed in system MTF from projection views between step-and-shoot mode and continuous motion mode while there was little difference in other measures from reconstruction slices. This system provides great flexibility for studying breast imaging and image quality under different acquisition protocols.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu, T., et al.: A comparison of reconstruction algorithms for breast tomosynthesis. Medical Physics 31(9), 2636–2647 (2004)
Sechopoulos, I., Ghetti, C.: Optimization of the acquisition geometry in digital tomosynthesis of the breast. Medical Physics 36(4), 1199–1207 (2009)
Zhang, Y., et al.: A comparative study of limited-angle cone-beam reconstruction methods for breast tomosynthesis. Medical Physics 33(10), 3781–3795 (2006)
Zhao, B., Zhao, W.: Imaging performance of an amorphous selenium digital mammography detector in a breast tomosynthesis system. Medical Physics 35(5), 1978–1987 (2008)
Li, B., et al.: The impact of acquisition angular range on the z-resolution of radiographic tomosynthesis. International Congress Series, vol. 1268, pp. 13–18 (2004)
Shaheen, E., Marshall, N., Bosmans, H.: Investigation of the effect of tube motion in breast tomosynthesis: continuous or step and shoot? SPIE (2011)
de las Heras Gala, H., et al. A versatile laboratory platform for studying x-ray 3D breast imaging. In: IEEE Medical Imaging Conference (2011)
Zeng, R., Myers, K.J.: Task-based comparative study of iterative image reconstruction methods for limited-angle x-ray tomography. SPIE (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Peng, R. et al. (2012). An Experimental Comparison of Continuous Motion and Step-and-Shoot Modes in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. In: Maidment, A.D.A., Bakic, P.R., Gavenonis, S. (eds) Breast Imaging. IWDM 2012. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7361. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31271-7_84
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31271-7_84
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-31270-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-31271-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)