Abstract
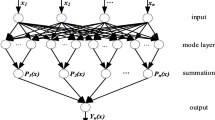
Load parameters inside the ball mill have direct relationships with the optimal operation of grinding process. This paper aims to develop a selective ensemble modeling approach to estimate these parameters. At first, the original vibration signal is decomposed into a number of intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) using empirical mode decomposition (EMD) adaptively. Then, frequency spectra of these IMFs are obtained via fast Fourier transform (FFT), and a serial of kernel partial least squares (KPLS) sub-models are constructed based on these frequency spectra. At last, the ensemble models are obtained by integrating the branch and band (BB) algorithm and the information entropy-based weighting algorithm. Experimental results based on a laboratory scale ball mill indicate that the propose approach not only has better prediction accuracy, but also can interpret the vibration signal more deeply.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou, P., Chai, T.Y., Wang, H.: Intelligent Optimal-Setting Control for Grinding Circuits of Mineral Processing. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering 6, 730–743 (2009)
Zeng, Y., Forssberg, E.: Monitoring Grinding Parameters by Vibration Signal Measurement-a Primary Application. Minerals Engineering 7, 495–501 (1994)
Gugel, K., Palcios, G., Ramirez, J., Parra, M.: Improving Ball Mill Control with Modern Tools Based on Digital Signal Processing (DSP) Technology. In: IEEE Cement Industry Technical Conference, pp. 311–318. IEEE Press, Dallas (2003)
Spencer, S.J., Campbell, J.J., Weller, K.R., Liu, Y.: Acoustic Emissions Monitoring of SAG Mill Performance. Intelligent Processing and Manufacturing of Materials 2, 936–946 (1999)
Tang, J., Zhao, L.J., Zhou, J.W., Yue, H., Chai, T.Y.: Experimental Analysis of Wet Mill Load Based on Vibration Signals of Laboratory-Scale Ball Mill Shell. Minerals Engineering 23, 720–730 (2010)
Tang, J., Zhao, L., Yu, W., Yue, H., Chai, T.: Soft Sensor Modeling of Ball Mill Load via Principal Component Analysis and Support Vector Machines. In: Zeng, Z., Wang, J. (eds.) Advances in Neural Network Research and Applications. LNEE, vol. 67, pp. 803–810. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Liu, J.L.: On-line Soft Sensor for Polyethylene Process with Multiple Production Grades. Control Engineering Practice 15, 769–778 (2007)
Huang, N.E., Shen, Z., Long, S.R.: The Empirical Mode Decomposition and the Hilbert Spectrum for Non-linear and Non Stationary Time Series Analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A. 454, 903–995 (1998)
McInerny, S.A., Dai, Y.: Basic Vibration Signal Processing for Bearing Fault Detection. IEEE Transactions on Education 46, 149–156 (2003)
Huang, P., Pan, Z.W., Qi, X.L., Lei, J.P.: Bearing Fault Diagnosis Based on EMD and PSD. In: Proceedings of the 8th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, pp. 1300–1304. IEEE Press, Ji Nan (2010)
Tang, J., Zhao, L.J., Yue, H., Yu, W., Chai, T.Y.: Vibration Analysis Based on Empirical Mode Decomposition and Partial Least Square. Procedia Engineering 16, 646–652 (2011)
Zhou, Z.H., Wu, J., Tang, W.: Ensembling Neural Networks: Many Could be Better Than All. Artificial Intelligence 137, 239–263 (2002)
Narendra, P.M., Fukunaga, K.: A Branch and Bound Algorithm for Feature Subset Selection. IEEE Transactions on Computers C-26, 917–922 (1977)
Wang, C.S., Wu, M., Cao, W.H., He, Y.: Intelligent Integrated Modeling and Synthetic Optimization for Blending Process in Lead-Zinc Sintering. Acta Automatica Sinica 35, 605–612 (2009)
Rosipal, R., Trejo, L.J.: Kernel Partial Least Squares Regression in Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2, 97–123 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tang, J., Zhao, LJ., Long, J., Chai, Ty., Yu, W. (2012). Selective Ensemble Modeling Parameters of Mill Load Based on Shell Vibration Signal. In: Wang, J., Yen, G.G., Polycarpou, M.M. (eds) Advances in Neural Networks – ISNN 2012. ISNN 2012. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7367. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31346-2_55
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31346-2_55
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-31345-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-31346-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)