Abstract
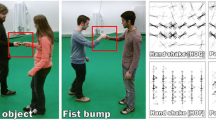
Automatic recovery of 3d pose of multiple interacting subjects from unconstrained monocular image sequence is a challenging and largely unaddressed problem. We observe, however, that by tacking the interactions explicitly into account, treating individual subjects as mutual “context” for one another, performance on this challenging problem can be improved. Building on this observation, in this paper we develop an approach that first jointly estimates 2d poses of people using multi-person extension of the pictorial structures model and then lifts them to 3d. We illustrate effectiveness of our method on a new dataset of dancing couples and challenging videos from dance competitions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andriluka, M., Roth, S., Schiele, B.: Monocular 3d pose estimation and tracking by detection. In: CVPR (2010)
Pellegrini, S., Edd, A., Schindler, K., van Gool, L.: You’ll never walk alone: Modeling social behaviour for multi-target tracking. In: ICCV (2009)
Yao, B., Fei-Fei, L.: Modeling mutual context of object and human pose in human-object interaction activities. In: CVPR (2010)
Kjellström, H., Kragic, D., Black, M.J.: Tracking people interacting with objects. In: CVPR (2010)
Ionescu, C., Bo, L., Sminchisescu, C.: Structured svm for visual localization and continuous state estimation. In: ICCV (2009)
Eichner, M., Ferrari, V.: We Are Family: Joint Pose Estimation of Multiple Persons. In: Daniilidis, K., Maragos, P., Paragios, N. (eds.) ECCV 2010. LNCS, vol. 6311, pp. 228–242. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Wang, J.M., Fleet, D.J., Hertzmann, A.: Gaussian process dynamical models for human motion. PAMI 30 (2008)
Felzenszwalb, P., Girshick, R., McAllester, D., Ramanan, D.: Object detection with discriminatively trained part based models. PAMI 32 (2010)
Andriluka, M., Roth, S., Schiele, B.: Pictorial structures revisited: People detection and articulated pose estimation. In: CVPR (2009)
Eichner, M., Ferrari, V.: Better appearance models for pictorial structures. In: BMVC (2009)
Ramanan, D.: Learning to parse images of articulated objects. In: NIPS (2006)
Felzenszwalb, P., Huttenlocher, D.: Pictorial structures for object recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision (2005)
Johnson, S., Everingham, M.: Clustered pose and nonlinear appearance models for human pose estimation. In: BMVC (2010)
Sapp, B., Weiss, D., Taskar, B.: Parsing human motion with stretchable models. In: CVPR (2011)
Yang, Y., Ramanan, D.: Articulated pose estimation with flexible mixtures-of-parts. In: CVPR (2011)
Ferrari, V., Marin-Jimenez, M., Zisserman, A.: Pose search: retrieving people using their pose. In: CVPR (2009)
Sigal, L., Black, M.J.: Measure locally, reason globally: Occlusion-sensitive articulated pose estimation. In: CVPR (2006)
Ferrari, V., Marin-Jimenez, M., Zisserman, A.: Progressive search space reduction for human pose estimation. In: CVPR (2008)
Tian, T.P., Sclaroff, S.: Fast globally optimal 2d human derection with loopy graph models. In: CVPR (2010)
Urtasun, R., Fleet, D., Fua, P.: 3d people tracking with gaussian process dynamical models. In: CVPR (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Andriluka, M., Sigal, L. (2012). Human Context: Modeling Human-Human Interactions for Monocular 3D Pose Estimation. In: Perales, F.J., Fisher, R.B., Moeslund, T.B. (eds) Articulated Motion and Deformable Objects. AMDO 2012. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7378. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31567-1_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31567-1_26
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-31566-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-31567-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)