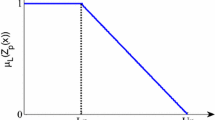
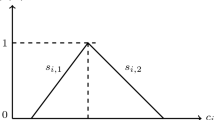
Abstract
The traditional frameworks for fuzzy linear optimization problems are inspired by the max-min model proposed by Zimmermann using the Bellman-Zadeh extension principle. This paper attempts to view fuzzy multiobjective linear programming problem (FMOLPP) from a perspective of preference modeling. The fuzzy constraints are viewed as negative preferences for rejecting what is unacceptable while the objective functions are viewed as positive preferences for depicting satisfaction to what is desired. This bipolar view enable us to handle fuzzy constraints and objectives separately and help to combine them in distinct ways. The optimal solution of FMOLPP is the one which maximizes the disjunctive combination of the weighted positive preferences provided it satisfy the negative preferences combined in conjunctive way.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atanassov, K.: Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets. Physica-Verlag, Heidelberg (1999)
Bellman, R.E., Zadeh, L.A.: Decision making in fuzzy environment. Management Sciences 17, B-141–B-164 (1970)
Benferhat, S., Dubois, D., Kaci, S., Prade, H.: Bipolar possibility theory in preference modeling: Representation, fusion and optimal solutions. Information Fusion 7, 135–150 (2006)
Cadenes, J.M., Jimènez, F.: Interactive decision making in multiobjective fuzzy programming. Mathware and Soft Computing 3, 210–230 (1994)
Dubois, D., Prade, H.: Possibility theory, probability theory and multiple-valued logics: a clarification. Annals Math. and Artificial Intelligence 32, 35–66 (2001)
Dubois, D., Prade, H.: Bipolar Representations in Reasoning, Knowledge Extraction and Decision Processes. In: Greco, S., Hata, Y., Hirano, S., Inuiguchi, M., Miyamoto, S., Nguyen, H.S., Słowiński, R. (eds.) RSCTC 2006. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 4259, pp. 15–26. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Liu, X.-W., Chen, L.H.: The equivalence of maximal entropy OWA operator and geometric OWA operator. In: Proceeding of the Second International Conference of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Xi’an, pp. 2673–2676 (2003)
O’Hagan, M.: Aggregating template or rule antecedents in real time expert systems with fuzzy set logic. In: Proceeding of 22nd Annual IEEE Asilomar Conf. Signals, Systems, Computers, Pacific Grove, pp. 681–689 (1988)
Sakawa, M., Inuiguchi, M.: A fuzzy satificing method for large- scale multiobjective linear programming problems with block angular structure. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 78, 279–288 (1996)
Sommer, G., Pollatschek, M.A.: A fuzzy programming approach to an air pollution regulation problem. Progress of Cybernetics and Systems Research III, 303–313 (1978)
Tsai, C.C., Chu, C.H., Barta, T.A.: Modelling and analysis of a manufacturing cell formation problem with fuzzy mixed integer programming. IIE Transactions 29, 533–547 (1997)
Tversky, A., Kahneman, D.: Advances in prospect theory: cumulative representation of uncertainty. Journal of Risk and Uncertainty 5, 297–323 (1992)
Werner, B.M.: Aggregation models in mathematical programming. In: Mitra, G. (ed.) Mathematical Models for Decision Support, pp. 295–305. Springer, Berlin (1988)
Yager, R.R.: On ordered weighted averaging aggregation operators in multicriteria decision making. IEEE Transaction on System, Man and Cybernetics 18, 183–190 (1988)
Yager, R.R.: Quantifier guided aggregation using OWA operators. Int. J. Intelligent Systems 11, 49–73 (1996)
Yager, R.R.: Constrained OWA aggregation. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 81, 89–101 (1996)
Zimmerman, H.-J.: Fuzzy programming and linear programming with several objective functions. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 1, 45–55 (1978)
Zimmerman, H.-J., Zysno, P.: Latent connectives in human decision making. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 4, 37–51 (1980)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dubey, D., Mehra, A. (2012). Fuzzy Multiobjective Linear Programming: A Bipolar View. In: Greco, S., Bouchon-Meunier, B., Coletti, G., Fedrizzi, M., Matarazzo, B., Yager, R.R. (eds) Advances in Computational Intelligence. IPMU 2012. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 300. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31724-8_48
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31724-8_48
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-31723-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-31724-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)