Abstract
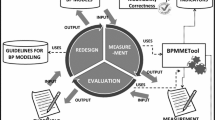
Business process improvement is a key aspect for organizational improvement. We focus the business process improvement in the first stage of process lifecycle, design stage, because it is a means to avoid the propagation of errors to later stages, in which their detection and correction may be more difficult. Since business process improvement is centered in business process models, a proposal of certain steps based on measurement activities on conceptual models (measurement, evaluation and redesign) is described. The application of these steps in business process models produces an increase of the quality of them. Quality is defined as the level of understandability and modifiability, subcharacteristics of the usability and maintainability in ISO 9126. The steps for model improvement have been applied to a real hospital business process model. The model was modified by following expert opinions and modeling guidelines, thus leading to the attainment of a higher-quality model. Our findings clearly support the practical utility of measurement activities for business process model improvement.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Damij, N., et al.: A methodology for business process improvement and IS development. Information and Software Technology 50(11), 1127–1141 (2008)
Cardoso, J.: Process control-flow complexity metric: An empirical validation. In: SCC 2006: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Services Computing, pp. 167–173 (2006)
Park, R.E., Goethert, W.B., Florac, W.A.: Goal-Driven software Measurement: A Guidebook. Handbook CMU/SEI-96-HB-002 (1996)
Weske, M.: Business Process Management: Concepts, Languages, Architectures, 1st edn. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Sparks, G.: An Introduction to UML, The Business Process Model. Enterprise Architect (2000)
Wand, Y., Weber, C.: Research commentary: Information systems and conceptual modeling–a research agenda. Info. Sys. Research 13(4), 363–376 (2002)
Sánchez-González, L., et al.: Measurement in Business Processes: a Systematic Review. Business Process Management Journal 16(1), 114–134 (2010)
Mendling, J.: Metrics for Process Models: Empirical Foundations of Verification, Error Prediction, and Guidelines for Correctness. Springer Publishing Company, Incorporated (2008)
Delgado, A., Ruiz, F., García-Rodríguez de Guzmán, I., Piattini, M.: MINERVA: Model drIveN and sErvice oRiented Framework for the Continuous Business Process improVement and relAted Tools. In: Dan, A., Gittler, F., Toumani, F. (eds.) ICSOC/ServiceWave 2009. LNCS, vol. 6275, pp. 456–466. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
ISO/IEC, 9126-1, Software engineering - product quality - Part 1: Quality Model (2001)
Moody, D.: Theoretical and practical issues in evaluating the quality of conceptual models: current state and future directions. Data and Knowledge Engineering 55, 243 (2005)
Lindland, O.I., Sindre, G., Solvberg, A.: Understanding Quality in Conceptual Modeling. IEEE Software 11(2), 42–49 (1994)
Shanks, G., Tansley, E., Weber, R.: Using ontology to validate conceptual models. Commun. ACM 46(10), 85–89 (2003)
Krogstie, J., et al.: Process models representing knowledge for action: a revised quality framework. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 15(1), 91–102 (2006)
Briand, L.C., Wüst, J., Ikonomovski, S., Lounis, H.: A Comprehensive Investigation of Quality Factors in Object-Oriented Designs. An Industrial Case Study. Technical Report ISERN-98-29 (1998)
Vanderfeesten, I., et al.: Quality Metrics for Business Process Models. In: BPM and Workflow Handbook (2007)
Vanderfeesten, I., Reijers, H.A., Mendling, J., van der Aalst, W.M.P., Cardoso, J.: On a Quest for Good Process Models: The Cross-Connectivity Metric. In: Bellahsène, Z., Léonard, M. (eds.) CAiSE 2008. LNCS, vol. 5074, pp. 480–494. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Rolón, E., García, F., Ruiz, F.: Evaluation Measures for Business Process Models. In: Simposioum in Applied Computing, SAC 2006 (2006)
Jung, J.Y.: Measuring entropy in business process models. International Conference on Innovative Computing. Information and Control, 246–252 (2008)
Laue, R., Mendling, J.: Structuredness and its Significance for Correctness of Process Models. Information Systems and E-Business Management (2009)
Meimandi Parizi, R., Ghani, A.A.A.: An Ensemble of Complexity Metrics for BPEL Web Processes. In: Ninth ACIS International Conference on Software Engineering, Artificial Intelligence, Networking, and Parallel/Distributed Computing, pp. 753–758 (2008)
Huan, Z., Kumar, A.: New quality metrics for evaluating process models. In: Business Process Intelligence Workshop (2008)
Rolon, E., et al.: Prediction Models for BPMN Usability and Maintainability. In: BPMN 2009 - 1st International Workshop on BPMN, pp. 383–390 (2009)
Sánchez González, L., et al.: Assessent and Prediction of Business Process Model Quality. In: CoopIS 2010 - 18th International Conference on Cooperative Information Systems, pp. 78–95 (2010)
Rolón, E., et al.: Analysis and Validation of Control-Flow Complexity Measures with BPMN Process Models. In: The 10th Workshop on Business Process Modeling, Development, and Support (2009)
McCabe, T.J.: A Complexity Measure. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering SE-2(4), 308–320 (1976)
Nejmeh, B.A.: NPATH: a Measure of Execution Path Complexity and its Applications. ACM 31(2), 188–200 (1988)
Coleman, D., Lowther, B., Oman, P.: The Application of Software Maintainability Models in Industrial Software Systems. Journal of Systems and Software 29(1), 3–16 (1995)
Shatnawi, R.: A Quantitative Investigation of the Acceptable Risk levels of Object-Oriented Metrics in Open-Source Systems. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering 36(2), 216–225 (2010)
Bender, R.: Quantitative Risk Assessment in Epidemiological Studies Investigatin Threshold Effects. Biometrical Journal 41(3), 305–319 (1999)
Sánchez-González, L., et al.: Towards Thresholds of Control Flow Complexity Measures for BPMN Models. In: 26th Symposium On Applied Computing. SAC, vol. 10 (in press, 2011)
Sánchez-González, L., et al.: Quality Assessment of Business Process Models Based on Thresholds. In: CoopIS 2010 - 18th International Conference on Cooperative Information Systems, pp. 78–95 (2010)
Mendling, J., Reijers, H.A., Van der Aalst, W.: Seven Process Modeling Guidelines (7PMG). Information and Software Technology 52(2), 127–136 (2010)
Becker, J., Rosemann, M., von Uthmann, C.: Guidelines of Business Process Modeling. In: van der Aalst, W.M.P., Desel, J., Oberweis, A. (eds.) Business Process Management. LNCS, vol. 1806, pp. 30–49. Springer, Heidelberg (2000)
OMG. Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN), Final Adopted Specification (2006), http://www.omg.org/bpm
Linstone, H.A., Turoff, M.: The Delphi Method: Techniques and Applications. Addison-Wesley (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sánchez-González, L., Ruiz, F., García, F., Piattini, M. (2013). Improving Quality of Business Process Models. In: Maciaszek, L.A., Zhang, K. (eds) Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering. ENASE 2011. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 275. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32341-6_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32341-6_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-32340-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-32341-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)