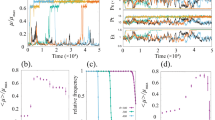
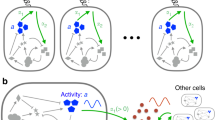
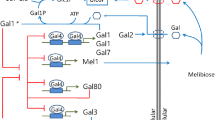
Abstract
Biological systems can generally adapt environmental chan- ges and to create symbiotic relationship with other species, by changing their intra-cellular states flexibly. However, the mechanisms for such flexible adaptation and creation of symbiotic relationship remain unclear. In this study, by using simple computer models of cells, we show that for cells whose gene expression fluctuate stochastically, the adaptive cellular state is inevitably selected by noise, even without sophisticated mechanisms. Furthermore, by the fluctuation-induced adaptation mechanism, we show that symbiotic relationships naturally appear in systems of interacting cells. This mechanism can provide clues to understand flexible adaptation and creation of symbiotic relationship. Applications of this mechanism for designing artificial systems are also discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacob, F., Monod, J.: Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 3, 318–356 (1961)
Kashiwagi, A., Urabe, I., Kaneko, K., Yomo, T.: Adaptive response of a gene network to environmental changes by fitness-induced attractor selection. PLoS One 1 e49 (2006)
Furusawa, C., Kaneko, K.: A Generic Mechanism for Adaptive Growth Rate Regulation. PLoS Comp. Biol. 4(1), e3 (2008)
Elowitz, M.B., Levine, A.J., Siggia, E.D., Swain, P.S.: A Generic Mechanism for Adaptive Growth Rate Regulation. Science 297, 1183–1186 (2002)
Kaern, M., Elston, T.C., Blake, W.J., Collins, J.J.: Stochasticity in gene expression: from theories to phenotypes. Nature Rev. Genet. 8, 451–464
Pedraza, J.M., Van Oudenaarden, A.: Nosise propagation in gene networks. Science 307, 1965–1969
Marr, A.G.: Growth rate of Escherichia coli. Microbio. Rev. 55(2), 316–333
Currie, C.R.: A community of ants, fungi, and bacteria: a multilateral approach to studying symbiosis. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 55, 357–380 (2001)
Minami, Y., Koizumi, Y., Arakawa, S., Murata, M.: Adaptability of Virtual Network Topology Control based on Attractor Selection. In: Proceedings of 2009 International Symposium on Nonlinear Theory and its Applications, NOLTA 2009 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 ICST Institute for Computer Science, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Furusawa, C., Ijichi, K., Shimizu, H. (2012). Fluctuation-Driven Adaptation and Symbiosis in Cellular Dynamics. In: Suzuki, J., Nakano, T. (eds) Bio-Inspired Models of Network, Information, and Computing Systems. BIONETICS 2010. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 87. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32615-8_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32615-8_25
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-32614-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-32615-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)