Abstract
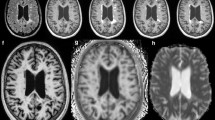
MR Images of the brain in Multiple Sclerosis (MS) show regions of signal abnormalities that can provide information for the diagnosis and for the pathogenesis of the disease. Two very commonly used MRI contrasts in this context are the T 1 weighted (T 1-w) and the FLAIR. This study shows that additional information can be extracted from the Susceptibility Weighted MRI (SWI) contrast. In particular, the signal and the contrast of white matter lesions in SWI are examined and compared to T 1-w and FLAIR contrasts. The lesions are analysed into hypo- and hyper-intense. Additionally, the spatial distributions for the two lesion types are computed and summarised with their expected distance from the ventricles. The data from 19 MS patients and 23 controls have been acquired and examined. The results show the presence of two lesion classes in SWI for MS patients, while T 1-w and FLAIR contrast mechanisms present only a single class each. The hypo-intense SWI lesions appear closer to the ventricles and are more correlated to the T 1-w signal rather than the FLAIR signal.
We acknowledge the funding support of the European Commission through the MIBISOC project (Marie Curie Initial Training Network, FP7 PEOPLE-ITN-2008, GA n. 238819).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dawson, J.: The histology of disseminated sclerosis. Trans. Roy. Soc. Edinb. 50, 517 (1916)
Evans, A., Collins, D., Mills, S., Brown, E., Kelly, R., Peters, T.: 3D statistical neuroanatomical models from 305 MRI volumes. In: Conference Record of Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, pp. 1813–1817. IEEE (1993)
Forbes, C., Evans, M., Hastings, N., Peacock, B.: Statistical distributions. Wiley Online Library (2011)
Friston, K.: Statistical parametric mapping: the analysis of functional brain images. Academic Press (2007)
Haacke, E., Makki, M., Ge, Y., Maheshwari, M., Sehgal, V., Hu, J., Selvan, M., Wu, Z., Latif, Z., Xuan, Y., et al.: Characterizing iron deposition in multiple sclerosis lesions using susceptibility weighted imaging. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 29(3), 537–544 (2009)
Haacke, E., Reichenbach, J., Xu, Y.: Susceptibility weighted imaging in MRI: basic concepts and clinical applications. Wiley (2011)
Hadjidemetriou, S., Buechert, M., Ludwig, U., Hennig, J.: Joint Restoration of Bi-contrast MRI Data for Spatial Intensity Non-uniformities. In: Székely, G., Hahn, H.K. (eds.) IPMI 2011. LNCS, vol. 6801, pp. 346–358. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Tan, I., van Schijndel, R., Pouwels, P., van Waldervenn, M., Reichenbach, J., Manoliu, R., Barkhof, F.: MR venography of multiple sclerosis. American Journal of Neuroradiology 21(6), 1039–1042 (2000)
Walderveen, M., Kamphorst, W., Scheltens, P.: Histopathologic correlate of hypo intense lesions in T1-weighted spin-echo MRI in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 50, 1282–1288 (1998)
Weinshenker, B., Bass, B., Rice, G., Noseworthy, J., Carriere, W., Baskerville, J., Ebers, G.: The natural history of multiple sclerosis: a geographically based study. Brain 112(1), 133–146 (1989)
Yao, B., Bagnato, F., Matsuura, E., Merkle, H., van Gelderen, P., Cantor, F., Duyn, J.: Chronic multiple sclerosis lesions: Characterization with high-field-strength MR imaging. Radiology 262(1), 206–215 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Strumia, M., Anastasopoulos, C., Mader, I., Henning, J., Bai, L., Hadjidemetriou, S. (2012). Comparative Characterisation of Susceptibility Weighted MRI for Brain White Matter Lesions in MS. In: Yap, PT., Liu, T., Shen, D., Westin, CF., Shen, L. (eds) Multimodal Brain Image Analysis. MBIA 2012. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7509. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33530-3_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33530-3_13
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-33529-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-33530-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)