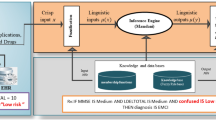
Abstract
The high mutability of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) leads to serious problems on designing efficient antiviral drugs. In fact, in last years the study of drug resistance prediction for HIV mutations has become an open problem for researchers. Several machine learning techniques have been proposed for modelling this sequence classification problem, but most of them are difficult to interpret. This paper presents a modelling of the protease protein as a dynamic system through Fuzzy Cognitive Maps, using the amino acid contact energies for the sequence description. In addition, a Particle Swarm Optimization based learning scheme called PSO-RSVN is used to estimate the causal weight matrix that characterize these structures. Finally, a study with statistical techniques for knowledge discovery is conducted, for determining patterns in the causal influences of each sequence position on the resistance to five well-known inhibitor drugs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prosperi, M., Ulivi, G.: Evolutionary Fuzzy Modelling for Drug Resistant HIV-1 Treatment Optimization. In: Abraham, A., Grosan, C., Pedrycz, W. (eds.) Engineering Evolutionary Intelligent Systems. SCI, vol. 82, pp. 251–287. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Beerenwinkel, N., et al.: Computational Methods for the Design of Effective Therapies Against Drug Resistant HIV Strains. Bioinformatics 21(21), 3943–3950 (2005)
Drǎghici, S., Potter, R.: Predicting HIV Drug Resistance with Neural Networks. Bioinformatics 19(1), 98–107 (2003)
Bonet, I., et al.: Predicting Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Drug Resistance Using Recurrent Neural Networks. In: Mira, J., Álvarez, J.R., et al. (eds.) IWINAC 2007. LNCS, vol. 4527, pp. 234–243. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Beerenwinkel, N., et al.: Geno2pheno: Interpreting Genotypic HIV Drug Resistance Tests. IEEE Intelligent Systems 16(6), 35–41 (2001)
Beerenwinkel, N., et al.: Diversity and Complexity of HIV-1 Drug Resistance A Bioinformatics Approach to Predicting Phenotype from Genotype. Proceedings of the National Academy of USA 99, 8271–8276 (2002)
Kosko, B.: Fuzzy Cognitive Maps. Intl. Journal of Man-Machine Studies 24, 65–75 (1986)
Kosko, B.: Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems, a Dynamic System Approach to Machine Intelligence. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1992)
Miyazawa, S., Jernigan, R.L.: Contacts Energies Self-Consistent Estimation of Inter-Residue Protein Contact Energies Based on an Equilibrium Mixture Approximation of Residues. PROTEINS: Structure, Function, and Genetics 34, 49–68 (1999)
McMichael, J.M., et al.: Optimizing Fuzzy Cognitive Maps with a Genetic Algorithm. In: AIAA 1st Intelligent Systems Technical Conference, Chicago, Illinois, pp. 1–11 (2004)
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.: Particle Swarm Optimization. In: 1995 IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks (ICNN 1995), vol. 4, pp. 1942–1948. IEEE (1995)
Bratton, D., Kennedy, J.: Defining a Standard for Particle Swarm Optimization. In: 2007 IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium (SIS 2007), pp. 120–127. IEEE (2007)
Clerc, M., Kennedy, J.: The Particle Swarm ( Explosion, Stability, and Convergence in a Multidimensional Complex Space. IEEE Trans. on Evolutionary Comp. 6(1), 58–73 (2002)
Kennedy, J., Russell, C.E.: Swarm Intelligence. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers (2001)
Nápoles, G., Grau, I., Bello, R.: Particle Swarm Optimization with Random Sampling in Variable Neighbourhoods for Solving Global Minimization Problems. In: Dorigo, M., Birattari, M., Blum, C., Christensen, A.L., Engelbrecht, A.P., Groß, R., Stützle, T. (eds.) ANTS 2012. LNCS, vol. 7461, pp. 352–353. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
León, M., Nápoles, G., et al.: Two Steps Individuals Travel Behavior Modeling through Fuzzy Cognitive Maps Pre-definition and Learning. In: Batyrshin, I., Sidorov, G. (eds.) MICAI 2011, Part II. LNCS, vol. 7095, pp. 82–94. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
León, M., Nápoles, G., et al.: A Fuzzy Cognitive Maps Modeling, Learning and Simulation Framework for Studying Complex System. In: Ferrández, J.M., Álvarez Sánchez, J.R., de la Paz, F., Toledo, F.J. (eds.) IWINAC 2011, Part II. LNCS, vol. 6687, pp. 243–256. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Stanford HIV Drug Resistance Database, http://hivdb.stanford.edu
Woods, M., Carpenter, G.A.: Neural Network and Bioinformatic Methods for Predicting HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor Resistance. CAS/CNS Technical Report 2007-004 (2007)
Witten, I.H., Frank, E., Hall, M.A.: Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques, 3rd edn. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers (2011)
Bonet, I.: Modelo para la Clasificación de Secuencias, en Problemas de la Bioinformática, Usando Técnicas de Inteligencia Artificial. PhD Thesis, UCLV (2008)
SPSS Inc.: The SPSS TwoStep Cluster Component. TSCWP-101 Technical Report (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Grau, I., Nápoles, G., León, M., Grau, R. (2012). Fuzzy Cognitive Maps for Modelling, Predicting and Interpreting HIV Drug Resistance. In: Pavón, J., Duque-Méndez, N.D., Fuentes-Fernández, R. (eds) Advances in Artificial Intelligence – IBERAMIA 2012. IBERAMIA 2012. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 7637. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34654-5_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34654-5_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-34653-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-34654-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)