Abstract
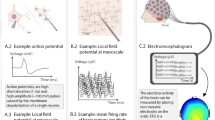
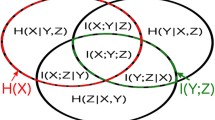
Inferring the interactions between different brain areas is an important step towards understanding brain activity. Most often, signals can only be measured from some specific brain areas (e.g., cortex in the case of scalp electroencephalograms). However, those signals may be affected by brain areas from which no measurements are available (e.g., deeper areas such as hippocampus). In this paper, the latter are described as hidden variables in a graphical model; such model quantifies the statistical structure in the neural recordings, conditioned on hidden variables, which are inferred in an automated fashion from the data.
As an illustration, electroencephalograms (EEG) of Alzheimer’s disease patients are considered. It is shown that the number of hidden variables in AD EEG is not significantly different from healthy EEG. However, there are fewer interactions between the brain areas, conditioned on those hidden variables. Explanations for these observations are suggested.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman, J., Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R.: Sparse inverse covariance estimation with the graphical lasso. Biostatistics 9, 432–441 (2008)
Chandrasekaran, V., Parrilo, P.A., Willsky, A.S.: Latent Variable Graphical Model Selection via Convex Optimization. Technical report, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2010)
Yu, H., Dauwels, J., Wang, X.O.: Copula Gaussian Graphical Models with Hidden Variables. In: Proc. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, pp. 2177–2180 (2012)
Billinger, D.R.: Remarks concerning graphical models for time series and point processes. Revista de Econometria 16, 1–23 (1996)
Dahlhaus, R.: Graphical interaction models for multivariate time series. Metrika 5, 157–172 (2000)
Bach, F.R., Jordan, M.I.: Learning graphical models for stationary time series. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 52, 2189–2199 (2004)
Dobra, A., Lenkoski, A.: Copula Gaussian graphical models and their application to modeling functional disability data. Annals of Applied Statistics 5, 969–993 (2011)
Liu, H., Lafferty, J., Wasserman, L.: The Nonparanormal: Semiparametric Estimation of High Dimensional Undirected Graphs. Journal of Machine Learning Research 10, 2295–2328 (2009)
Wang, C., Sun, D., Toh, K.C.: Solving log-determinant optimization problems by a Newton-CG primal proximal point algorithm. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics 20, 2994–3013 (2009)
Henderson, G., Ifeachor, E., Hudson, N., Goh, C., Outram, N., Wimalaratna, S., Del Percio, C., Vecchio, F.: Development and assessment of methods for detecting dementia using the human electroencephalogram. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 53, 1557–1568 (2006)
Dauwels, J., Vialatte, F., Cichocki, A.: Diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease from EEG signals: Where are we standing? Current Alzheimer Research 7, 487–505 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dauwels, J. et al. (2012). Inferring Brain Networks through Graphical Models with Hidden Variables. In: Langs, G., Rish, I., Grosse-Wentrup, M., Murphy, B. (eds) Machine Learning and Interpretation in Neuroimaging. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 7263. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34713-9_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34713-9_25
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-34712-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-34713-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)