Abstract
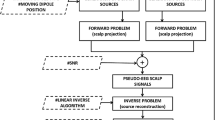
We consider the problem of estimating brain effective connectivity from electroencephalographic (EEG) measurements, which is challenging due to instantaneous correlations in the sensor data caused by volume conduction in the head. We present selected results of a larger realistic simulation study in which we tested the ability of various measures of effective connectivity to recover the information flow between the underlying sources, as well as the ability of linear and nonlinear inverse source reconstruction approaches to improve the estimation. It turns out that factors related to volume conduction dramatically limit the neurophysiological interpretability of sensor-space connectivity maps and may even (depending on the connectivity measure used) lead to conflicting results. The success of connectivity estimation on inverse source estimates crucially depends on the correctness of the source demixing. This in turn depends on the capability of the method to model (multiple) interacting sources, which is in general not achievable by linear inverses.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baccalá, L.A., Sameshima, K.: Partial directed coherence: a new concept in neural structure determination. Biol. Cybern. 84, 463–474 (2001)
Granger, C.W.J.: Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross-spectral methods. Econometrica 37, 424–438 (1969)
Haufe, S., Tomioka, R., Dickhaus, T., Sannelli, C., Blankertz, B., Nolte, G., Müller, K.-R.: Large-scale EEG/MEG source localization with spatial flexibility. NeuroImage 54, 851–859 (2011)
Haufe, S.: Towards EEG source connectivity analysis. PhD thesis, Berlin Institute of Technology (2011)
Haufe, S., Nikulin, V.V., Nolte, G.: Alleviating the Influence of Weak Data Asymmetries on Granger-Causal Analyses. In: Theis, F., Cichocki, A., Yeredor, A., Zibulevsky, M. (eds.) LVA/ICA 2012. LNCS, vol. 7191, pp. 25–33. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Ioannides, A.A., Bolton, J.P.R., Clarke, C.J.S.: Continous probabilistic solutions to the biomagnetic inverse problem. Inverse Probl. 6, 523–542 (1990)
Nolte, G., Ziehe, A., Nikulin, V.V., Schlögl, A., Krämer, N., Brismar, T., Müller, K.R.: Robustly estimating the flow direction of information in complex physical systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 234101 (2008)
Supp, G.G., Schlögl, A., Trujillo-Barreto, N., Müller, M.M., Gruber, T.: Directed cortical information flow during human object recognition: analyzing induced EEG gamma-band responses in brain’s source space. PLoS ONE 2, e684 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Haufe, S., Nikulin, V.V., Nolte, G., Müller, KR. (2012). Pitfalls in EEG-Based Brain Effective Connectivity Analysis. In: Langs, G., Rish, I., Grosse-Wentrup, M., Murphy, B. (eds) Machine Learning and Interpretation in Neuroimaging. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 7263. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34713-9_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34713-9_26
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-34712-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-34713-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)