Abstract
Many model based techniques have been proposed in the literature for applying domestic service tasks on humanoid robots, such as teleoperation, learning from demonstration and imitation. However sensor based robot control overcomes many of the difficulties of uncertain models and unknown environments which limit the domain of application of the previous methods. Furthermore, for service and manipulation tasks, it is more suitable to study the interaction between the robot and its environment at the contact point using the sensor based control, rather than specifying the joint positions and velocities required to achieve them.
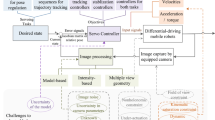
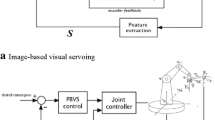
In this work we present an integration of real-time visual servoing techniques on a humanoid robot in closed loop, to perform self-localization and different manipulation tasks. Indeed, real-time model based tracking techniques are used to apply 3D visual servoing tasks on the Nao humanoid robot. The elementary tasks which are used by the robot to perform a concrete service scenario are detailed with their corresponding control laws. Finally, we present the experimental results of the following tasks: self-localization of the robot while walking, head servoing for the visibility task, detection, tracking and manipulation of environment’s objects.
This research has been partially funded by the French National Agency of Research under the reference ANR-10-SEGI-002, and partially by Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (DPI2011-27846), Generalitat Valenciana (PROMETEO/2009/052) and Fundació CaixaCastelló-Bancaixa (P1-1B2011-54).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brock, O., Kuffner, J., Xiao, J.: Motion for manipulation tasks. In: Siciliano, B., Khatib, O. (eds.) Springer Handbook of Robotics, pp. 615–645. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Evrard, P., Mansard, N., Stasse, O., Kheddar, A., Schau, T., Weber, C., Peer, A., Buss, M.: Intercontinental, multimodal, wide-range telecooperation using a humanoid robot. In: IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems - IROS 2009, pp. 5635–5640 (2009)
Nitzsche, N., Schmidt, G.: A mobile haptic interface mastering a mobile teleoperator. In: IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems - IROS 2004, vol. 4, pp. 3912–3917 (September-October 2004)
Houston, K., Sieber, A., Eder, C., Vittorio, O., Menciassi, A., Dario, P.: A teleoperation system with novel haptic device for micromanipulation. Int. Journal of Robotics and Automation 26(3) (2011)
Miller, W.T.: Sensor-based control of robotic manipulators using a general learning algorithm. IEEE Journal of Robotics and Automation 3(2), 157–165 (1987)
Dang, H., Allen, P.: Robot learning of everyday object manipulations via human demonstration. In: IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems - IROS 2010, pp. 1284–1289 (October 2010)
Jain, A., Kemp, C.: Pulling open novel doors and drawers with equilibrium point control. In: IEEE-RAS Int. Conf. on Humanoid Robots, pp. 498–505 (December 2009)
Mansard, N., Stasse, O., Chaumette, F., Yokoi, K.: Visually-guided grasping while walking on a humanoid robot. In: IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 3041–3047 (April 2007)
Quinlan, M.J., Middleton, R.H.: Multiple Model Kalman Filters: A Localization Technique for RoboCup Soccer. In: Baltes, J., Lagoudakis, M.G., Naruse, T., Ghidary, S.S. (eds.) RoboCup 2009. LNCS, vol. 5949, pp. 276–287. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Billington, D., Estivill-Castro, V., Hexel, R., Rock, A.: Using Temporal Consistency to Improve Robot Localisation. In: Lakemeyer, G., Sklar, E., Sorrenti, D.G., Takahashi, T. (eds.) RoboCup 2006. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 4434, pp. 232–244. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Haverinen, J., Kemppainen, A.: Global indoor self-localization based on the ambient magnetic field. Int. Journal of Robotics and Autonomous Systems 57(10), 1028–1035 (2009)
Thuilot, B., Martinet, P., Cordesses, L., Gallice, J.: Position based visual servoing: keeping the object in the field of vision. In: IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, vol. 2 (2002)
Gouaillier, D., Hugel, V., Blazevic, P., Kilner, C., Monceaux, J., Lafourcade, P., Marnier, B., et al.: Mechatronic design of Nao humanoid. In: IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 769–774 (May 2009)
Chaumette, F., Hutchinson, S.: Visual servo control. i. basic approaches. IEEE Robotics Automation Magazine 13(4), 82–90 (2006)
Cervera, E.: A Cross-Platform Network-Ready Visual Servo Simulator. In: IEEE Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2006), Beijing (China), pp. 2314–2319 (2006)
Marchand, E., Spindler, F., Chaumette, F.: Visp for visual servoing: a generic software platform with a wide class of robot control skills. IEEE Robotics Automation Magazine 12, 40–52 (2005)
Comport, A., Marchand, E., Pressigout, M., Chaumette, F.: Real-time markerless tracking for augmented reality: the virtual visual servoing framework. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 12(4), 615–628 (2006)
Galindo, C., Fernandez-Madrigal, J.-A., Gonzalez, J., Saffiotti, A.: Robot task planning using semantic maps. Robotics and Autonomous Systems 56(11), 955–966 (2008)
Stasse, O., Verrelst, B., Vanderborght, B., Yokoi, K.: Strategies for humanoid robots to dynamically walk over large obstacles. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 25(4), 960–967 (2009)
Sorribes, J., Prats, M., Morales, A.: Visual tracking of a jaw gripper based on articulated 3d models for grasping. In: IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 2302–2307 (May 2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Moughlbay, A.A., Cervera, E., Martinet, P. (2013). Model Based Visual Servoing Tasks with an Autonomous Humanoid Robot. In: Lee, S., Yoon, KJ., Lee, J. (eds) Frontiers of Intelligent Autonomous Systems. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 466. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-35485-4_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-35485-4_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-35484-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-35485-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)