Abstract
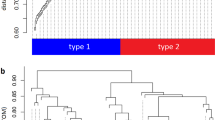
Gene expression profiles produced by Microarray present a potential method for exploring the relationship between genes and brain. Here we analyzed the human gene expression levels among eight brain regions, including frontal lobe, Insula, limblic lobe, occipital lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, basal ganglia and other cerebral nuclei. Top 45 schizophrenia candidate genes(179 probes) expression levels were compared between each two of these regions. Strikingly, 66.7% gene(83.2% probe) expression in basal ganglia distinguished from other regions. The great variation of the schizophrenia candidate gene expression in different brain regions indicated there is different neuropathologic mechanisms regulated by these candidate genes to this disease and basal ganglia would be the expression center of schizophrenia candidate genes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, M.R., Huxley-Jones, J., Maycox, P.R., et al.: Transcription and pathway analysis of the superior temporal cortex and anterior prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. Journal of Neuroscience Research 89(8), 1218–1227 (2011)
Vawter, M.P., Crook, J.M., Hyde, T.M., et al.: Microarray analysis of gene expression in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia: a preliminary study. Schizophrenia Research 58(1), 11–20 (2002)
Potkin, S.G., Turner, J.A., Brown, G.G., et al.: Working memory and dlpfc inefficiency in schizophrenia: the fbirn study. Schizophr. Bull. 35(1), 19–31 (2009)
Bowden, N.A., Scott, R.J., Tooney, P.A.: Altered gene expression in the superior temporal gyrus in schizophrenia. Bmc Genomics 9, 199 (2008)
Lauriat, T.L., Shiue, L., Haroutunian, V., et al.: Developmental expression profile of quaking, a candidate gene for schizophrenia, and its target genes in human prefrontal cortex and hippocampus shows regional specificity. J. Neurosci. Res. 86(4), 785–796 (2008)
Melendez, R.I., McGinty, J.F., Kalivas, P.W., et al.: Brain region-specific gene expression changes after chronic intermittent ethanol exposure and early withdrawal in c57bl/6j mice. Addict. Biol. 17(2), 351–364 (2012)
Liang, M., Zhou, Y., Jiang, T., et al.: Widespread functional disconnectivity in schizophrenia with resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroreport 17(2), 209–213 (2006)
Allen, N.C., Bagade, S., McQueen, M.B., et al.: Systematic meta-analyses and field synopsis of genetic association studies in schizophrenia: the szgene database. Nat. Genet. 40(7), 827–834 (2008)
Mah, S., Nelson, M.R., Delisi, L.E., et al.: Identification of the semaphorin receptor plxna2 as a candidate for susceptibility to schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 11(5), 471–478 (2006)
Takeshita, M., Yamada, K., Hattori, E., et al.: Genetic examination of the plxna2 gene in japanese and chinese people with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 99(1-3), 359–364 (2008)
Oertel-Knochel, V., Knochel, C., Matura, S., et al.: Cortical-basal ganglia imbalance in schizophrenia patients and unaffected first-degree relatives. Schizophrenia Research 138(2-3), 120–127 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lu, X., Liu, P., Zeng, Ll., Li, R., Hu, D. (2013). Schizophrenia Candidate Genes Specific to Human Brain Region Are Restricted to Basal Ganglia. In: Yang, J., Fang, F., Sun, C. (eds) Intelligent Science and Intelligent Data Engineering. IScIDE 2012. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7751. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-36669-7_69
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-36669-7_69
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-36668-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-36669-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)