Abstract
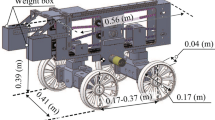
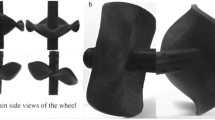
In the future, the planetary exploration missions, planetary robots are required to traverse over very rough terrain. On the lunar surface and Mars surface, there are covered with loose soil, namely “Regolith”. The reason why the wheel is easy to occur the poor condition during traverse on loose soil is not yet clear in detail. We use Terramechanics model for analyzing the mechanism of slipping and sinking behavior. Terramechanics model which is widely used as locomotion model for some lunar rovers is applicable to only circular wheel. So, it is not easy to apply to wheel with grousers. Therefore, firstly, we simulated the conventional model to confirm the defference between the wheel without grousers and with grousers. Secondly, we carry out the running experiments using the rigid circular wheel (with and without grousers) to compare with simulation results. From these results, we consider the difference between the conventional model and the real wheel’s model.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mars Pathfinder, http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/MPF/
MARS Rover, http://marsrover.nasa.gov/home/index.html
Iizuka, K., Kanamori, H., Kubota, T.: A Study of Terramechanics for Movement on Planetary Surface. Robotics Symposia 10, 33–38 (2005) (in Japanese)
European Space Agency, http://www.esa.int/esaMI/ExoMars/index.html
Michelin Group, http://www.michelin.com/
Yon, R.N., Fattah, E.A., Skidas, N., Kitano, M.: Run dynamics of off-road vehicles. The Japanese Society for Study Technology Education (1986)
Iagnemma, K., Kang, S., Shibly, H., Dubowsky, S.: Online Terrain Parameter Estimation for Wheeled Mobile Robots With Application to Planetary robots. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 20(5), 921–927 (2004)
Yoshida, K., Hamano, H.: Motion Dynamics Simulations and Experiments of an Exploration robot on Natural Terrain. In: The 11th Workshop on Astrodynamics and Flight Mechanics, pp. 306–313 (2001)
Iizuka, K., Kanamori, H., Kubota, T.: Wheeled Running Experiment with Mimic Physiognomy of Moon by Planetary Explore Robots. In: Conf. on Robotics and Mechatronics, No. 5 (2005) (in Japanese)
Sutoh, M., Nagatani, K., Yoshida, K.: Evaluation of influence of surface shape of wheel on traveling performance of planetary rovers over slope. In: Proc. of 17th Internal Conference of the International Society for Terrain-Vehicle Systems, pp. 18–22 (2011)
Nakashima, H., Fujii, H., Oida, A., Momozu, M., Kanamori, H., Aoki, S., Yokoyama, T., Shimizu, H., Miyasaka, J., Ohdoi, K.: Discrete element method analysis of single wheel performance for a small lunar rover on sloped terrain. Journal of Terramechanics 47(5), 307–321 (2010)
Irani, R.A., Bauer, R.J., Warkentin, A.: A dynamic terramechanic model for small lightweight vehicles with rigid wheels and grousers operating in sandy soil. Journal of Terramechanics 48(4), 307–318 (2011)
Obermayr, M., Dressler, K., Vrettos, C., Eberhard, P.: Prediction of draft forces in cohesionless soil with the Discrete Element Method. Journal of Terramechanics 48(5), 347–358 (2011)
Lyasko, M.: Slip sinkage effect in soil-vehicle mechanics. Journal of Terramechanics 47(1), 21–31 (2010)
Ding, L., Gao, H., Deng, Z., Nagatani, K., Yoshida, K.: Experimental study and analysis on driving wheels’ performance for planetary rovers moving in deformable soil. Journal of Terramechanics 48(1), 27–45 (2011)
Bekker, M.: Theory of Land Locomotion. The University of Michigan Press (1955)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Nakane, Y., Iizuka, K., Kubota, T. (2013). Experimental Study of Grouser’s Effect for Planetary Rovers Based on Terramechanics. In: Kim, JH., Matson, E., Myung, H., Xu, P. (eds) Robot Intelligence Technology and Applications 2012. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 208. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-37374-9_61
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-37374-9_61
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-37373-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-37374-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)