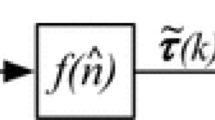
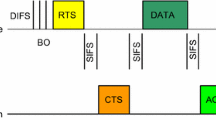
Abstract
A distributed medium-access control (MAC) protocol for the time-slotted channel with multi-packet reception (MPR) capability is proposed. In contrast to the commonly assumed collision channel, in the MPR channel with channel capacity K, it is possible to decode up to K packets whose transmissions overlap in time. In order to exploit the MPR capability, the additive-increase multiplicative-decrease MAC (AIMD-MAC) protocol is designed to adaptively adjust the access probabilities of the independent nodes based on their local transmission histories. The examined performance metrics for evaluating this protocol include aggregate throughput, average packet delay and system fairness. Extensive simulations show that the performance of AIMD-MAC is superior to that of S-Aloha* under light traffic loads and achieves the optimum level after the system is saturated. With a suitable parameter set, AIMD-MAC can be adequately applied in a dynamic wireless environment.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertsekas, D., Gallager, R.: Data networks, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River (1992)
Celik, G.D., Zussman, G., Khan, W.F., Modiano, E.: Mac for networks with multipacket reception capability and spatially distributed nodes. Mobile Computing 9(2), 226–240 (2010)
Chan, D.S., Berger, T.: Performance and cross-layer design of csma for wireless networks with multipacket reception. In: Proc. IEEE Asilomar, vol. 2, pp. 1917–1921 (November 2004)
Chiu, D., Jain, R.: Analysis of the increase and decrease algorithms for congestion avoidance in computer networks. Comput. Netw. ISDN Syst. (June 1989)
Cleary, A.C., Paterakis, M.: An investigation of reservation random access algorithms for voice-data integration in microcellular wireless environments. In: IEEE Globecom (November 1994)
Ghanbarinejad, M., Schlegel, C., Gburzynski, P.: Adaptive probabilistic medium access in mpr-capable ad-hoc wireless networks. In: Proc. of the IEEE Global Telecommunication Conference, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA (2009)
Ghez, S., Verdu, S., Schwartz, S.C.: Stability properties of slotted aloha with multipacket reception capability. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 33, 640–649 (1988)
Guo, M., Wang, X., Wu, M.: On the capacity of k-mpr wireless networks. Wireless Communications 8(7), 3878–3886 (2009)
Heusse, M., Rousseau, F., Guillier, R., Duda, A.: Idle sense: an optimal access method for high throughput and fairness in rate diverse wireless lans. In: ACM SIGCOMM (2005)
Holland, G., Vaidya, N., Bahl, P.: A rate-adaptive mac protocol for multi-hop wireless networks. Mobile Computing and Networking (2001)
Hou, T.-C., Lucantoni, D.M.: Buffer sizing for synchronous self-routing broadband packet switches with bursty traffic. International Journal of Digital and Analog Cabled Communication 2(1), 253–260 (1989)
Hu, C., Hou, J.C.: A novel approach to contention control in ieee 802.11e-operated wlans. In: IEEE INFOCOM, pp. 1190–1198 (May 2007)
Jacobson, V.: Congestion avoidance and control. In: SIGCOMM, Stanford, California, USA, pp. 314–329 (1988)
Jain, R., Chiu, D., Hawe, W.: A quantitative measure of fairness and discrimination for resource allocation in shared computer systems. Computing Research Repository, cs.NI/9809 (1998)
Jung, E., Vaidya, N.: A power control mac protocol for ad hoc networks. Wireless Networks 11, 55–66 (2005)
Kwack, S., Seo, H., Lee, B.: Suitability-based subcarrier allocation for multicast services employing layered video coding in wireless ofdm systems. In: Vehicular Technology Conference, pp. 1752–1756 (October 2007)
Lous, N.J.C., Bours, P.A.H., van Tilborg, H.C.A.: On maximum likelihood soft-decision decoding of binary linear codes. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 39(1), 197–203 (1993)
Mergen, G., Tong, L.: Receiver controlled medium access in multihop ad hoc networks with multipacket reception. In: Military Communications Conference, vol. 2, pp. 1014–1018 (2001)
Schlegel, C., Grant, A.: Coordinated multiuser communications. Springer (2006)
LAN/MAN standards Committee, et al.: Information Technology – Telecommunications and Information Exchange Between Systems – Local and Metropolitan Area Networks – Specific Requirements: Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications. IEEE Std. IEEE (1997)
Tong, L., Zhao, Q., Mergen, G.: Multipacket reception in random access wireless networks: from signal processing to optimal medium access control. IEEE Communications Magazine 39(11), 108–112 (2001)
Van Dam, T., Langendoen, K.: An adaptive energy-efficient mac protocol for wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, SenSys 2003, Los Angeles, California, USA, pp. 171–180 (2003)
Weber, S.P., Andrews, J.G., Yang, X., de Veciana, G.: Transmission capacity of wireless ad hoc networks with successive interference cancellation. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 53(8), 2799–2814 (2007)
Ye, W., Heidemann, J., Estrin, D.: An energy-efficient mac protocol for wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Infocom, pp. 1567–1576 (June 2002)
Zhao, Q., Tong, L.: A multiqueue service room mac protocol for wireless networks with multipacket reception. IEEE/ACM Trans. Networking 11, 125–137 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, K., Ghanbarinejad, M., Nikolaidis, I., Schlegel, C. (2013). Additive-Increase Multiplicative-Decrease MAC Protocol with Multi-Packet Reception. In: Tsaoussidis, V., Kassler, A.J., Koucheryavy, Y., Mellouk, A. (eds) Wired/Wireless Internet Communication. WWIC 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7889. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-38401-1_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-38401-1_2
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-38400-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-38401-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)