Abstract
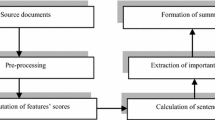
This paper describes experiments to adapt document summarization to the medical domain. Our summarizer combines linguistic features corresponding to text fragments (typically sentences) and applies a machine learning approach to extract the most important text fragments from a document to form a summary. The generic features comprise features used in previous research on summarization. We propose to adapt the summarizer to the medical domain by adding domain-specific features. We explore two types of additional features: medical domain features and semantic features. The evaluation of the summarizer is based on medical articles and targets different aspects: i) the classification of text fragments into ones which are important and ones which are unimportant for a summary; ii) analyzing the effect of each feature on the performance; and iii) system improvement over our baseline summarizer when adding features for domain adaptation. Evaluation metrics include accuracy for training the sentence extraction and the ROUGE measure computed for reference summaries. We achieve an accuracy of 84.16% on medical balanced training data by using an IB1 classifier. Training on unbalanced data achieves higher accuracy than training on balanced data. Domain adaptation using all domain-specific features outperforms the baseline summarization wrt. ROUGE scores, which shows the successful domain adaptation with simple means.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hovy, E., Lin, C.Y.: Automated text summarization in SUMMARIST. In: Mani, I., Maybury, M.T. (eds.) Advances in Automatic Text Summarization. MIT Press (1999)
Luhn, H.P.: The automatic creation of literature abstracts. IBM Journal of Research and Development 2(2), 159–165 (1958)
Edmundson, H.P.: New methods in automatic extracting. Journal of the ACM 16(2), 264–285 (1969)
Paice, C.D.: The automatic generation of literature abstracts: An approach based on the identification of self-indicating phrases. In: SIGIR 1981, pp. 172–191 (1981)
Nenkova, A., McKeown, K.: Foundations and trends in information retrieval. Automatic Summarization 5, 103–233 (2011)
Das, D., Martins, A.F.: A survey on automatic text summarization. Technical report, Literature Survey for the Language and Statistics II course at Carnegie Mellon University (2007)
Nenkova, A.: Automatic text summarization of newswire: lessons learned from the document understanding conference. In: AAAI 2005, pp. 1436–1441. AAAI Press (2005)
Conroy, J.M., O’Leary, D.P.: Text summarization via Hidden Markov Models. In: SIGIR 2001, pp. 406–407 (2001)
Lin, C.Y.: Training a selection function for extraction. In: Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, CIKM 1999, pp. 55–62. ACM, New York (1999)
Kupiec, J., Pedersen, J., Chen, F.: A trainable document summarizer. In: Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 68–73 (1995)
McKeown, K., Chang, S.F., Cimino, J., Feiner, S., Friedman, C., Gravano, L., Hatzivassiloglou, V., Johnson, S., Jordan, D., Klavans, J., Kushniruk, A., Patel, V., Teufel, S.: PERSIVAL, a system for personalized search and summarization over multimedia healthcare information. In: ACM/IEEE-CS Joint Conference on Digital Libraries, pp. 331–340 (2001)
Yang, J., Cohen, A., Hersh, W.: Automatic summarization of mouse gene information by clustering and sentence extraction from MEDLINE abstracts. In: AMIA Annual Symposium, pp. 831–835 (2007)
Gupta, V., Lehal, G.: A survey of text summarization extractive techniques. Journal of Emerging Technologies in Web Intelligence 2(3) (2010)
Salton, G., Singhal, A., Mitra, M., Buckley, C.: Automatic text structuring and summarization. Inf. Process. Manage. 33(2), 193–207 (1997)
Brandow, R., Mitze, K., Rau, L.F.: Automatic condensation of electronic publications by sentence selection. Inf. Process. Manage. 31(5), 675–685 (1995)
Litvak, M., Last, M.: Graph-based keyword extraction for single-document summarization. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Multi-source Multilingual Information Extraction and Summarization. MMIES 2008, pp. 17–24. Association for Computational Linguistics, Stroudsburg (2008)
Patwardhan, S., Banerjee, S., Pedersen, T.: Using measures of semantic relatedness for word sense disambiguation. In: Gelbukh, A. (ed.) CICLing 2003. LNCS, vol. 2588, pp. 241–257. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Banerjee, S., Pedersen, T.: An adapted lesk algorithm for word sense disambiguation using wordNet. In: Gelbukh, A. (ed.) CICLing 2002. LNCS, vol. 2276, pp. 136–145. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Lin, D.: An Information-Theoretic Definition of Similarity. In: Shavlik, J.W., Shavlik, J.W. (eds.) ICML, pp. 296–304. Morgan Kaufmann (1998)
Plaza, L., Díaz, A., Gervás, P.: Automatic summarization of news using Wordnet concept graphs. In: Proceedings of the IADIS International Conference Informatics, pp. 19–26 (2009)
Fattah, M.A., Ren, F.: Ga, mr, ffnn, pnn and gmm based models for automatic text summarization. Computer Speech & Language 23(1), 126–144 (2009)
Lin, C.Y.: Rouge: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In: Proc. ACL Workshop on Text Summarization Branches Out, p. 10 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nguyen, D.T., Leveling, J. (2013). Exploring Domain-Sensitive Features for Extractive Summarization in the Medical Domain. In: Métais, E., Meziane, F., Saraee, M., Sugumaran, V., Vadera, S. (eds) Natural Language Processing and Information Systems. NLDB 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7934. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-38824-8_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-38824-8_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-38823-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-38824-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)