Abstract
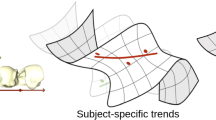
Hierarchical linear models (HLMs) are a standard approach for analyzing data where individuals are measured repeatedly over time. However, such models are only applicable to longitudinal studies of Euclidean data. In this paper, we propose a novel hierarchical geodesic model (HGM), which generalizes HLMs to the manifold setting. Our proposed model explains the longitudinal trends in shapes represented as elements of the group of diffeomorphisms. The individual level geodesics represent the trajectory of shape changes within individuals. The group level geodesic represents the average trajectory of shape changes for the population. We derive the solution of HGMs on diffeomorphisms to estimate individual level geodesics, the group geodesic, and the residual geodesics. We demonstrate the effectiveness of HGMs for longitudinal analysis of synthetically generated shapes and 3D MRI brain scans.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnol’d, V.I.: Sur la géométrie différentielle des groupes de Lie de dimension infinie et ses applications à l’hydrodynamique des fluides parfaits. Ann. Inst. Fourier 16, 319–361 (1966)
Beg, M., Miller, M., Trouvé, A., Younes, L.: Computing large deformation metric mappings via geodesic flows of diffeomorphisms. IJCV 61(2), 139–157 (2005)
Durrleman, S., Pennec, X., Trouvé, A., Gerig, G., Ayache, N.: Spatiotemporal atlas estimation for developmental delay detection in longitudinal datasets. In: Yang, G.-Z., Hawkes, D., Rueckert, D., Noble, A., Taylor, C. (eds.) MICCAI 2009, Part I. LNCS, vol. 5761, pp. 297–304. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Fishbaugh, J., Prastawa, M., Durrleman, S., Piven, J., Gerig, G.: Analysis of longitudinal shape variability via subject specific growth modeling. In: Ayache, N., Delingette, H., Golland, P., Mori, K. (eds.) MICCAI 2012, Part I. LNCS, vol. 7510, pp. 731–738. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Fletcher, P.T.: Geodesic regression on Riemannian manifolds. In: MICCAI Workshop on Mathematical Foundations of Computational Anatomy, pp. 75–86 (2011)
Laird, N.M., Ware, J.H.: Random-effects models for longitudinal data. Biometrics 38(4), 963–974 (1982)
Lorenzi, M., Ayache, N., Frisoni, G.B., Pennec, X., The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: Mapping the Effects of Aβ 1−42 Levels on the Longitudinal Changes in Healthy Aging: Hierarchical Modeling Based on Stationary Velocity Fields. In: Fichtinger, G., Martel, A., Peters, T. (eds.) MICCAI 2011, Part II. LNCS, vol. 6892, pp. 663–670. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Miller, M.I., Trouvé, A., Younes, L.: Geodesic shooting for computational anatomy. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision 24(2), 209–228 (2006)
Muralidharan, P., Fletcher, P.: Sasaki metrics for analysis of longitudinal data on manifolds. In: IEEE Conference on CVPR, pp. 1027–1034 (June 2012)
Niethammer, M., Huang, Y., Vialard, F.-X.: Geodesic regression for image time-series. In: Fichtinger, G., Martel, A., Peters, T. (eds.) MICCAI 2011, Part II. LNCS, vol. 6892, pp. 655–662. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Singh, N., Hinkle, J., Joshi, S., Fletcher, P.T.: A vector momenta formulation of diffeomorphisms for improved geodesic regression and atlas construction. In: International Symposium on Biomedial Imaging (ISBI) (April 2013)
Younes, L., Arrate, F., Miller, M.I.: Evolution equations in computational anatomy. Neuroimage 45(1 suppl.), S40–S50 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Singh, N., Hinkle, J., Joshi, S., Fletcher, P.T. (2013). A Hierarchical Geodesic Model for Diffeomorphic Longitudinal Shape Analysis. In: Gee, J.C., Joshi, S., Pohl, K.M., Wells, W.M., Zöllei, L. (eds) Information Processing in Medical Imaging. IPMI 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7917. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-38868-2_47
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-38868-2_47
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-38867-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-38868-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)