Abstract
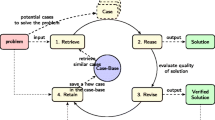
Case-Base Maintenance (CBM) has two important goals. On the one hand, it aims to reduce the size of the case-base. On the other hand, it has to improve the accuracy of the CBR system. CBM can be represented as a multi-objective optimization problem to achieve both goals. Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithms (MOEAs) have been recognised as appropriate techniques for multi-objective optimisation because they perform a search for multiple solutions in parallel. In the present paper we introduce a fitness function based on the Complexity Profiling model to perform CBM with MOEA, and we compare its results against other known CBM approaches. From the experimental results, CBM with MOEA shows regularly good results in many case-bases, despite the amount of redundant and noisy cases, and with a significant potential for improvement.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brighton, H., Mellish, C.: On the consistency of information filters for lazy learning algorithms. In: Żytkow, J.M., Rauch, J. (eds.) PKDD 1999. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 1704, pp. 283–288. Springer, Heidelberg (1999)
Coello, C.C., Lamont, G., van Veldhuizen, D.: Evolutionary Algorithms for Solving Multi-Objective Problems. Genetic and Evolutionary Computation (2007)
Cover, T., Hart, P.: Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 13(1), 21–27 (1967)
Cummins, L., Bridge, D.: Maintenance by a committee of experts: The MACE approach to case-base maintenance. In: McGinty, L., Wilson, D.C. (eds.) ICCBR 2009. LNCS, vol. 5650, pp. 120–134. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., Meyarivan, T.: A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 6(2) (2002)
Frank, A., Asuncion, A.: UCI machine learning repository (2010), http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml
Gates, G.: Reduced nearest neighbor rule. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 18(3), 431 (1972)
Hart, P.: Condensed nearest neighbor rule. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 14(3), 515+ (1968)
Holland, J.H.: Adaptation in Natural And Artificial Systems. MIT Press (1975)
Ishibuchi, H., Nakashima, T., Nii, M.: Genetic-algorithm-based instance and feature selection. In: Frasson, C., McCalla, G.I., Gauthier, G. (eds.) ITS 1992. LNCS, vol. 608, pp. 95–112. Springer, Heidelberg (1992)
Cano, J.R., Herrera, F., Lozano, M.: Evolutionary stratified training set selection for extracting classification rules with trade off precision-interpretability. Data & Knowledge Engineering 60(1), 90–108 (2007)
Kim, K., Han, I.: Maintaining case-based reasoning systems using a genetic algorithms approach. Expert Systems with Applications 21(3), 139–145 (2001)
Leake, D., Wilson, M.: How many cases do you need? Assessing and predicting case-base coverage. In: Ram, A., Wiratunga, N. (eds.) ICCBR 2011. LNCS, vol. 6880, pp. 92–106. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Leake, D.B., Wilson, D.C.: Categorizing case-base maintenance: Dimensions and directions. In: Smyth, B., Cunningham, P. (eds.) EWCBR 1998. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 1488, pp. 196–207. Springer, Heidelberg (1998)
Massie, S., Craw, S., Wiratunga, N.: Complexity-guided case discovery for case based reasoning. In: 20th National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI 2005, vol. 1, pp. 216–221 (2005)
Massie, S., Craw, S., Wiratunga, N.: Complexity profiling for informed case-base editing. In: Roth-Berghofer, T.R., Göker, M.H., Güvenir, H.A. (eds.) ECCBR 2006. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 4106, pp. 325–339. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
McKenna, E., Smyth, B.: Competence-guided case-base editing techniques. In: Blanzieri, E., Portinale, L. (eds.) EWCBR 2000. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 1898, pp. 186–197. Springer, Heidelberg (2000)
Pan, R., Yang, Q., Pan, S.: Mining competent case bases for case-based reasoning. Artificial Intelligence 171(16-17), 1039–1068 (2007)
Smyth, B., Keane, M.: Remembering to forget - a competence-preserving case deletion policy for case-based reasoning systems. In: International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI 1995, pp. 377–382 (1995)
Smyth, B., McKenna, E.: Competence guided incremental footprint-based retrieval. Knowledge-Based Systems 14(3-4), 155–161 (2001)
Wilson, D.: Asymptotic properties of nearest neighbor rules using edited data. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics SMC 2(3), 408 (1972)
Wilson, D., Martinez, T.: Reduction techniques for instance-based learning algorithms. Machine Learning 38(3), 257–286 (2000)
Zitzler, E., Thiele, L.: Multiobjective evolutionary algorithms: A comparative case study and the strength pareto approach. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 3(4), 257–271 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lupiani, E., Craw, S., Massie, S., Juarez, J.M., Palma, J.T. (2013). A Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithm Fitness Function for Case-Base Maintenance. In: Delany, S.J., Ontañón, S. (eds) Case-Based Reasoning Research and Development. ICCBR 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 7969. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39056-2_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39056-2_16
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-39055-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-39056-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)