Abstract
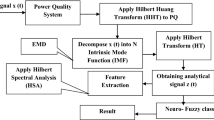
Based on intrinsic mode functions (IMFs), standard energy difference of each IMF obtained by EEMD and probabilistic neural network (PNN), a new method is proposed to the recognition of power quality transient disturbances. In this method, ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) is used to decompose the non-stationary power quality disturbances into a number of IMFs. Then the standard energy differences of each IMF are used as feature vectors. At last, power quality disturbances are identified and classified with PNN. The experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively realize feature extraction and classification of single and mixed power quality disturbances.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, G.-B., Xiang, D.-Y., Ma, W.-M.: Improved Algorithm for Noninteger Harmonics Analysis Based on FFT Algorithm and Neural Network. Proceedings of the CSEE 28(4), 102–108 (2008)
Lin, S., He, Z., Luo, G.: A wavelet energy moment based classification and recognition method of transient signals in power transmission lines. Power System Technology 32(20), 30–34 (2008)
Li, T., Zhao, Y., Li, N., et al.: A new method for power quality detection based on HHT. Proceedings of the CSEE 25(17), 52–56 (2005)
Bulus-Rossinia, L.A., Costanzo-Casoa, P.A., Duchowicza, R., et al.: Optical pulse compression using the temporal Radon–Wigner transform. Optics Communications 283, 2529–2535 (2010)
Yi, J.-L., Peng, J.-C., Tan, H.-S.: A summary of S-transform applied to power quality disturbances analysis. Power System Protection and Control 39(3), 141–147 (2011)
Styvaktakis, E., Boolen, M.J., Gu, I.Y.H.: Expert system for classification and analysis of power system events. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 17(2), 423–428 (2002)
Song, X.-F., Chen, J.-C.: Classification method of dynamic power quality disturbances based on SVM. Electric Power Automation Equipment 26(4), 39–42 (2006)
Yao, J.-G., Guo, Z.-F., Chen, J.-P.: A New Approach to Recognize Power Quality Disturbances Based on Wavelet Transform and BP Neural Network. Power System Technology 36(5), 139–144 (2012)
Huang, N.E., Shen, Z., Long, S.R., et al.: The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A 45(4), 903–995 (1998)
Huang, N.E., Shen, Z., et al.: The empirical code decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for non-linear and non-stationary time series analysis. Royal Society 454, 915–995 (1998)
Wu, Z., Huang, N.E.: Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition: A Noise Assisted Data Analysis Method. Center for Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Studies (2009)
Zhang, Y., Liu, Z.: Application of EEMD in power quality disturbance detection. Electric Power Automation Equipment 31(12), 86–91 (2011)
Kou, J., Xiong, S., Wan, S., Liu, H.: The Incremental Probabilistic Neural Network. In: Sixth International Conference on Natural Computation, pp. 1330–1333 (2010)
Wahab, N.I.A., Mohamed, A.: Transient Stability Assessment of a Large Actual Power System using Probabilistic Neural Network with Enhanced Feature Selection and Extraction. In: International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics, pp. 519–524 (2009)
Chowdhury, H.B.: Power quality. IEEE Potentials 20(2), 5–11 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhu, L., Liu, Z., Zhang, Q., Hu, Q. (2013). An Approach of Power Quality Disturbances Recognition Based on EEMD and Probabilistic Neural Network. In: Guo, C., Hou, ZG., Zeng, Z. (eds) Advances in Neural Networks – ISNN 2013. ISNN 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7951. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39065-4_61
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39065-4_61
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-39064-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-39065-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)