Abstract
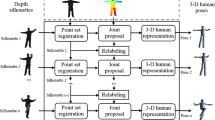
We present a system for markerless human motion capture through a hierarchical method from multiple camera views. In the absence of markers, the task of recovering the human pose is challenging and requires strong image features and robust algorithm. We propose a solution which integrates the 2D posture information and the volumetric reconstruction. Firstly, the model’s initia posture is obtained through the method of segmenting silhouette. After that, we track the human pose by using a hierarchical method, which is divided into three steps: head detection, torso prediction and limb matching. In order to gain the robust results, we discard the interior voxel data, use the middle voxel data for motion tracking, and use the surface voxel data for global optimization. The experiment results show that the method is valid and robust.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mykhaylo, A., Stefan, R., Bernt, S.: Monocular 3D pose estimation and tracking by detection. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 623–630 (2010)
Ankur, A., Bill, T.: Recovering 3D human pose from monocular images. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 28, 44–58 (2006)
Atul, K., Niels, H., Graham, T., et al.: 3D human pose and shape estimation from multi-view imagery. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 49–56 (2011)
Hofmann, M., Gavrila, D.M.: Multi-view 3D human pose estim-ation in complex environment. International Journal of Computer Vision 96, 103–124 (2012)
Smith, B.A.: Model Free Human Pose Estimation with Application to the Classification of Abnormal Human Movement and the Detection of Hidden Load. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Virginia (2010)
Caillette, F., Howard, T.: Real-Time Marklerless Human Body Tracking with Multi-View 3-D Voxel Reconstruction. In: Proc. BMVC, vol. 2, pp. 597–606 (2004)
Gall, J., Potthoff, J., Schnörr, C., Rosenhahn, B., Seidel, H.-P.: Interacting and annealing particle filters: Mathematics and a recipe for applications. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 1–18 (2007)
Kaliamoorthi, P., Kakarala, R.: Human pose tracking by parametric annealing. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop (2012)
Sigal, L., Isard, M., Haussecker, H., Black, M.J.: Loose-limbed People: Estimating 3D Human Pose and Motion Using Non-Parametric Belief Propagation. Internal Journal of Computer Vision 98, 15–48 (2012)
Zhang, Z., Seah, H.S., Quah, C.K.: Particle swarm optimization for markerless full body motion capture. In: Panigrahi, B.K., Shi, Y., Lim, M.-H. (eds.) Handbook of Swarm Intelligence. ALO, vol. 8, pp. 201–220. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Kehl, R., Van Gool, L.: Markerless tracking of complex human motions from multiple views. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 104, 190–209 (2006)
Shen, J.-F., Yang, W.-M., Liao, Q.-M.: Multiview human pose estimation with unconstrained motions. Pattern Recognition Letters 32, 2025–2035 (2011)
Zhang, Z.Y.: A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 22, 1330–1334 (1998)
Cheung, K.M., Kanade, T., Bouguet, J.-Y., Holler, M.: A Real-Time System for robust 3D voxel reconstruction of human motions. In: CVPR, vol. 2, pp. 714–720 (2000)
Sigal, L., Balan, A.O., Black, M.J.: HumanEva: Synchronized video and motion capture dataset and baseline algorithm for evaluation of articulated human motion. International Journal of Computer Vision 87, 4–27 (2010)
Poppe, R.: Evaluating example-based pose estimation: Experiments on the HumanEva sets. In: CVPR EhuM2: 2nd Workshop on Evaluation of Articulated Human Moition and Pose Estimation (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lei, Y., Pan, H., Chen, W., Gao, C. (2013). A New Hierarchical Method for Markerless Human Pose Estimation. In: Chen, M., Leibe, B., Neumann, B. (eds) Computer Vision Systems. ICVS 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7963. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39402-7_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39402-7_17
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-39401-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-39402-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)