Abstract
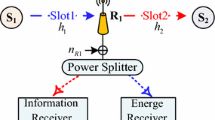
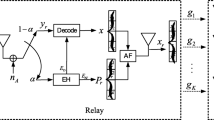
In this paper, the two-way opportunistic amplify-and-forward relaying system with multi-source multi-relay in underground tunnel is investigated; in which two sources intend to exchange information with help of one relay. The joint source-relay selection with power allocation is proposed to minimize the total transmit power subject to constraints on the received signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) of each source node. We show that this problem has a closed-form solution and requires only a few parameters to be broadcasted to all relays during the source-relay selection period. Simulation results show that the outage probability can be substantially decreased using the proposed power allocation scheme when two source node have different quality of service (QoS) requirement, comparing to existing power allocation algorithms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, Z., Akyildiz, I.F., Hancke, G.P.: Capacity and outage analysis of MIMO and cooperative communication systems in underground tunnels. IEEE Trans. on Wireless Communications 10(11), 3793–3803 (2011)
Funian, L., Desheng, Z.G.W.: Optimal power allocation for two-way relaying over OFDM using physical-layer network coding. Journal of China Universities of Posts and Telecommunications 18(1), 9–15 (2011)
Chen, D., Azarian, K., Laneman, J.N.: A case for amplify-forward relaying in the block-fading multiple-access channel. IEEE Transaction on Information Theory 54(8), 3728–3733 (2008)
Rankov, B., Wittneben, A.: Spectral efficient protocols for half-duplex fading relay channel. IEEE Journal Selected Areas Communications 25(2), 379–389 (2007)
Louie, R., Li, Y., Vucetic, B.: Practical physical layer network coding for two-way relay channels: Performance analysis and comparison. IEEE Transaction on Wireless Communications 9(2), 764–777 (2010)
Jing, Y., Jafarkhani, H.: Single and multiple-relay-selection schemes and their diversity orders. IEEE Transaction on Wireless Communications 8(3), 1414–1423 (2009)
Jing, Y.: A relay selection scheme for two-way amplify-and-forward relay networks. In: Proc. IEEE 2009 Wireless Communication and Signal Processing, Nanjing, China, November 13-15, pp. 1–5 (2009)
Song, L.: Relay Selection for two-way relay with amplify-and-forward protocols. IEEE Transaction on Vehicular Technology 60(4), 1954–1959 (2011)
Zhang, X., Gong, Y.: Adaptive power allocation in two-way amplify-and-forward relay networks. In: Proc. IEEE 2009 International Conference Communications (ICC 2009), Dresden, Germany, June 14-18, vol. 4, pp. 1–5 (2009)
Liu, T.C.-K., Xu, W., Dong, X., Lu, W.-S.: Adaptive power allocation for bidirectional amplify-and-forward multiple-relay multiple user networks. In: Proc. IEEE Globe Telecommunications Conference (GLOBECOM 2010), Miami, America, December 6-10, pp. 1–6 (2010)
Han, Y., Ting, S., Ho, C., Chin, W.: High-rate two-way amplify-and-forward half-duplex relaying with OSTBC. In: Proc. IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC 2008), Marina Bay, Singapore, May 11-16, pp. 2426–2430 (2008)
Zhang, Y., Ma, Y., Tafazolli, R.: Power allocation for bidirectional AF relaying over Rayleigh fading channels. IEEE Communication Letter 14(2), 145–147 (2010)
Talwar, S., Jing, Y., Shahbazpanahi, S.: Joint relay selection and power allocation for two-way relay networks. IEEE Signal Process Letter 18, 91–94 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, S., Sun, Y., Ma, R. (2013). A Source-Relay Selection Scheme with Power Allocation for Asymmetric Two-Way Relaying Networks in Underground Mines. In: Ren, K., Liu, X., Liang, W., Xu, M., Jia, X., Xing, K. (eds) Wireless Algorithms, Systems, and Applications. WASA 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 7992. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39701-1_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39701-1_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-39700-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-39701-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)