Abstract
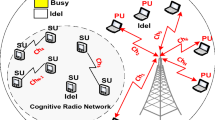
The medium access control (MAC) of decentralized cognitive radio networks has been a topic of interest in the last years due to the lack of a central coordinator and the necessity of self-organizing procedures that effectively lead the nodes to act autonomously but efficiently. This work addresses a scenario where multiple non-licensed cognitive radios communicate with an access point when licensed users do not use the spectrum. We consider a MAC protocol for the non-licensed users which uses a double stage to schedule each node’s transmission. Non-licensed users perform spectrum sensing in a synchronous way and the proposed MAC is opportunistically employed when the channel is sensed idle. In the first stage the number of competing non-licensed nodes is decreased to reduce the number of collisions. In the second stage we adopt a reservation procedure to schedule the non-licensed users competing for the medium. Adopting a traditional energy-based sensing, we characterize the performance of the considered protocol by capturing the influence of the sensing in the MAC’s performance. Finally we present several results to evaluate the performance of the proposed scheme achieved in optimal conditions, which are compared to a cognitive ”slotted-aloha”-like protocol. The obtained results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed solution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao, Q., Tong, L., Swami, A., Chen, Y.: Decentralized cognitive mac for opportunistic spectrum access in ad hoc networks: A pomdp framework. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 25(3), 589–600 (2007)
Yucek, T., Arslan, H.: A survey of spectrum sensing algorithms for cognitive radio applications. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials 11, 116–130 (2009)
Hsu, A.-C., Wei, D.S.L., Kuo, C.-C.: A cognitive mac protocol using statistical channel allocation for wireless ad-hoc networks. In: Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, WCNC 2007, pp. 105–110. IEEE (2007)
Lien, S.-Y., Tseng, C.-C., Chen, K.-C.: Carrier sensing based multiple access protocols for cognitive radio networks. In: IEEE International Conference on Communications, ICC 2008, pp. 3208–3214 (2008)
Chen, Q., Liang, Y.-C., Motani, M., Wong, W.-C.: A two-level mac protocol strategy for opportunistic spectrum access in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 60(5), 2164–2180 (2011)
Luis, M., Furtado, A., Oliveira, R., Dinis, R., Bernardo, L.: Towards a realistic primary users’ behavior in single transceiver cognitive networks. IEEE Communications Letters 17(2), 309–312 (2013)
Urkowitz, H.: Energy Detection of Unknown Deterministic Signals. Proceedings of the IEEE 55, 523–531 (1967)
Digham, F., Alouini, M.-S., Simon, M.: On the energy detection of unknown signals over fading channels. In: Proc. IEEE ICC 2003, pp. 3575–3579 (May 2003)
Tang, H.: Some physical layer issues of wide-band cognitive radio systems. In: Proc. IEEE DySPAN 2005, pp. 151–159 (November 2005)
Luis, M., Furtado, A., Oliveira, R., Dinis, R., Bernardo, L.: Energy sensing parameterization criteria for cognitive radios. In: 2012 International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS), pp. 61–65 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Luís, M., Oliveira, R., Dinis, R., Bernardo, L. (2013). Optimization of a Decentralized Medium Access Control Scheme for Single Radio Cognitive Networks. In: Balandin, S., Andreev, S., Koucheryavy, Y. (eds) Internet of Things, Smart Spaces, and Next Generation Networking. ruSMART NEW2AN 2013 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 8121. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40316-3_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40316-3_23
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-40315-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-40316-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)