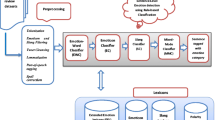
Abstract
Traditional methods for sentiment analysis mainly focus on the construction of emotional resources based on the review corpus of specific areas, and use phrase matching technologies to build a list of product feature words and opinion words. These methods bring about the disadvantages of inadequate model scalability, low matching precision, and high redundancy. Besides, it is particularly difficult to deal with negative words. In this work, we designed a unified framework based on finite state matching machine to deal with the problems of emotional element extraction. The max-matching principal and negative words processing can be integrated into the framework naturally. In addition, the framework leverages rule-based methods to filter out illegitimate feature-opinion pairs. Compared with traditional methods, the framework achieves high accuracy and scalability in emotional element extraction. Experimental results show that the extracting accuracy is up to 84%, which has increased by 20% comparing with traditional phrase matching techniques.
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation (60903107, 61073071) and National High Technology Research and Development (863) Program (2011AA01A205) of China.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
: 中国互联网络信息中心(CNNIC). 第31次中国互联网络发展状况统计报告 1 (2013), http://www.cnnic.cn/hlwfzyj/hlwxzbg/hlwtjbg/201301/P020130122600399530412.pdf
Yu, H., Hatzivassiloglou, V.: Towards answering opinion questions: Separating facts from opinions and identifying the polarity of opinion sentences. In: Proceedings of the 2003 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 129–136. Association for Computational Linguistics (2003)
Ku, L.W., Liang, Y.T., Chen, H.H.: Opinion extraction, summarization and tracking in news and blog corpora. In: Proceedings of AAAI-2006 Spring Symposium on Computational Approaches to Analyzing Weblogs (2001, 2006)
Dave, K., Lawrence, S., Pennock, D.M.: Mining the peanut gallery: Opinion extraction and semantic classification of product reviews. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 519–528. ACM (2003)
Kim, S.M., Hovy, E.: Determining the sentiment of opinions. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, p. 1367. Association for Computational Linguistics (2004)
Liu, B., Hu, M., Cheng, J.: Opinion observer: analyzing and comparing opinions on the Web. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 342–351. ACM (2005)
李智超,面向互联网评论的情感资源构建及应用研究. 北京:清华大学计算机科学与技术系, 4 (2011)
Hu, M., Liu, B.: Mining opinion features in customer reviews. In: Proceedings of the National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 755–760. AAAI Press, MIT Press, Menlo Park, Cambridge (1999, 2004)
Hu, M., Liu, B.: Mining and summarizing customer reviews. In: Proceedings of the Tenth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 168–177. ACM (2004)
Popescu, A.M., Etzioni, O.: Extracting product features and opinions from reviews. In: Natural Language Processing and Text Mining, pp. 9–28. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Hiroshi, K., Tetsuya, N., Hideo, W.: Deeper sentiment analysis using machine translation technology. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, p. 494. Association for Computational Linguistics (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tan, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, M., Liu, Y., Ma, S. (2013). A Unified Framework for Emotional Elements Extraction Based on Finite State Matching Machine. In: Zhou, G., Li, J., Zhao, D., Feng, Y. (eds) Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing. NLPCC 2013. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 400. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-41644-6_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-41644-6_7
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-41643-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-41644-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)