Abstract
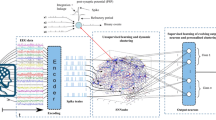
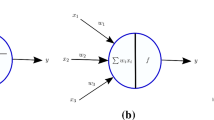
A vast amount of complex spatio-temporal brain data, such as EEG-, have been accumulated. Technological advances in many disciplines rely on the proper analysis, understanding and utilisation of these data. In order to address this great challenge, the paper utilizes the recently introduced by one of the authors 3D spiking neural network environment called NeuCube for spatio-temporal EEG data classification. A methodology is proposed and illustrated on two small-scale examples: classifying EEG data for music- versus noise perception, and person identification based on music perception. Future development and usage of the NeuCube environment can be expected to significantly further the creation of novel brain-computer interfaces, cognitive robotics and medical engineering devices.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zillies, K., Amunts, K.: Centenary of Brodmann’s map – conception and fate. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 11, 139–145 (2010)
Talairach, J., Tournoux, P.: Co-planar Stereotaxic Atlas of the Human Brain: 3-Dimensional Proportional System - an Approach to Cerebral Imaging. Thieme Medical Publishers, NY (1988)
Evans, A.C., Collins, D.L., Mills, S.R., et al.: 3D statistical neuroanatomical models from 305 MRI volumes. In: Proc. IEEE-Nuclear Science Symp. Medical Imaging Conference, pp. 1813–1817 (1993)
Toga, A., Thompson, P., Mori, S., et al.: Towards multimodal atlases of the human brain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 7, 952–966 (2006)
Abeles, M.: Corticonics. Cambridge University Press, NY (1991)
Fiasché, M., Schliebs, S., Nobili, L.: Integrating Neural Networks and Chaotic Measurements for Modelling Epileptic Brain. In: Villa, A.E.P., Duch, W., Érdi, P., Masulli, F., Palm, G. (eds.) ICANN 2012, Part I. LNCS, vol. 7552, pp. 653–660. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Lotte, F., Congedo, M., Lécuyer, A., Lamarche, F., et al.: A review of classification algorithms for EEG-based brain-computer interfaces. J. Neural Eng. 4(2), 1–15 (2007)
Stam, C.J.: Functional connectivity patterns of human magnetoencephalographic recordings: A small-world network? Neurosci. Lett. 355, 25–28 (2004)
De Charms, R.C.: Applications of real-time fMRI. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 9, 720–729 (2008)
Mitchel, T., Hutchinson, R., et al.: Learning to Decode Cognitive States from Brain Images. Machine Learning 57, 145–175 (2004)
Broderson, K., Wiech, K., Lomakina, E., et al.: Decoding the perception of pain from fMRI using multivariate pattern analysis. NeuroImage 63, 1162–1170 (2012)
Hawrylycz, M., et al.: An anatomically comprehensive atlas of the adult human brain transcriptome. Nature 489, 391–399 (2012)
Gerstner, W., Sprekeler, H., Deco, G.: Theory and simulation in neuroscience. Science 338, 60–65 (2012)
Song, S., Miller, K., Abbott, L., et al.: Competitive hebbian learning through spike-timing-dependent synaptic plasticity. Nature Neuroscience 3, 919–926 (2000)
Thorpe, S., Gautrais, J.: Rank order coding. Comput. Neuroscience: Trends in Research 13, 113–119 (1998)
Maass, W., Natschlaeger, T., Markram, H.: Real-time computing without stable states: A new framework for neural computation based on perturbations. Neural Computation 14(11), 2531–2560 (2002)
Izhikevich, E.: Polychronization: Computation with Spikes. Neural Computation 18, 245–282 (2006)
Belatreche, A., Maguire, L.P., McGinnity, M.: Advances in Design and Application of Spiking Neural Networks. Soft Comput. 11(3), 239–248 (2006)
Gerstner, W.: What’s different with spiking neurons? In: Mastebroek, H., Vos, H. (eds.) Plausible Neural Networks for Biological Modelling, pp. 23–48. Kluwer Academic Publishers (2001)
Lichtsteiner, P., Posch, C., Delbruck, T.: A 128x128 120dB 30mW Asynchronous Vision Sensor that Responds to Relative Intensity Changes. ISSCC Digest of Technical Papers, pp. 508–509 (2006)
Liu, S.C., Delbruck, T.: Neuromorphic sensory systems. Curr. Opinion in Neurobiology 20(3), 288–295 (2010)
Benuskova, L., Kasabov, N.: Computational neuro-genetic modelling. Springer, New York (2007)
Kasabov, N.: To spike or not to spike: A probabilistic spiking neuron model. Neur. Netw. 23(1), 16–19 (2010)
Furber, S.: To Build a Brain. IEEE Spectrum 49(8), 39–41 (2012)
Indiveri, G., Horiuchi, T.K.: Frontiers in neuromorphic engineering. Frontiers in Neuroscience 5, 1–2 (2011)
Kasabov, N., Dhoble, K., Nuntalid, N., Indiveri, G.: Dynamic Evolving Spiking Neural Networks for On-line Spatio- and Spectro-Temporal Pattern Recognition. Neural Networks 41, 188–201 (2013)
Mohemmed, A., Schliebs, S., Matsuda, S., Kasabov, N.: SPAN: Spike Pattern Association Neuron for Learning Spatio-Temporal Sequences. Int. J. of Neural Systems 22(4), 1–16 (2012)
Kasabov, N.: NeuCube EvoSpike Architecture for Spatio-Temporal Modelling and Pattern Recognition of Brain Signals. In: Mana, N., Schwenker, F., Trentin, E. (eds.) ANNPR 2012. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 7477, pp. 225–243. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Kasabov, N.: Evolving connectionist systems: The knowledge engineering approach. Springer (2007)
Koessler, L., Maillard, L., Benhadid, A., et al.: Automated cortical projection of EEG sensors: Anatomical correlation via the international 10–10 system. NeuroImage 46, 64–72 (2006)
Kasabov, N.: Evolving Spiking Neural Networks and Neurogenetic Systems for Spatio- and Spectro-Temporal Data Modelling and Pattern Recognition. In: Liu, J., Alippi, C., Bouchon-Meunier, B., Greenwood, G.W., Abbass, H.A. (eds.) WCCI 2012. LNCS, vol. 7311, pp. 234–260. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kasabov, N., Hu, J., Chen, Y., Scott, N., Turkova, Y. (2013). Spatio-temporal EEG Data Classification in the NeuCube 3D SNN Environment: Methodology and Examples. In: Lee, M., Hirose, A., Hou, ZG., Kil, R.M. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 8228. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-42051-1_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-42051-1_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-42050-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-42051-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)