Abstract
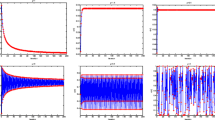
This paper discusses the energy minimization problem of a class of chaotic systems, and constructs an optimal neuro-controller based on adaptive dynamic programming (ADP) algorithm. To learn the optimal performance index and control policy, an iterative algorithm is established. To prove the convergence of the presented iterative algorithm, theorems with rigorous and detailed proofs are given. It is proven that the iterative performance index functions are monotone decreasing and converge to the minimum energy. A simulation example is used to indicate that the presented energy minimization control method is effective.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, H., Huang, W., Wang, Z., Chai, T.: Adaptive synchronization between two different chaotic systems with unknown parameters. Physics Letters A 350(5-6), 363–366 (2006)
Chen, S., Lü, J.: Synchronization of an uncertain unified chaotic system via adaptive control 14(4), 643–647 (2002)
Zhang, H., Wang, Z., Liu, D.: Chaotifying fuzzy hyperbolic model using adaptive inverse optimal control approach 14(10), 3505–3517 (2004)
Ma, T., Fu, J.: Global exponential synchronization between L system and Chen system with unknown parameters and channel time-delay. Chinese Physics B 20(5), 050511 (2011)
Ma, T., Fu, J., Sun, Y.: An improved impulsive control approach to robust lag synchronization between two different chaotic systems. Chinese Physics B 19(9), 090502 (2010)
Ma, T., Zhang, H., Fu, J.: Exponential synchronization of stochastic impulsive perturbed chaotic Lur’e systems with time-varying delay and parametric uncertainty. Chinese Physics B 17(12), 4407–4417 (2008)
Zhang, H., Ma, T., Fu, J., Tong, S.: Robust lag synchronization of two different chaotic systems via dual-stage impulsive control. Chinese Physics B 18(9), 3751–3757 (2009)
Song, R., Xiao, W., Sun, C., Wei, Q.: Approximation-Error-ADP-Based Optimal Tracking Control for Chaotic Systems With Convergence Proof. Chinese Physics B (accept)
Murray, J., Cox, C., Lendaris, G., Saeks, R.: Adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C: Applications and Reviews 32(2), 140–153 (2002)
Seiffertt, J., Sanyal, S., Wunsch, D.: Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equations and approximate dynamic programming on time scales. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics 38(4), 918–923 (2008)
He, P., Jagannathan, S.: Reinforcement learning neural-network-based controller for nonlinear discrete-time systems with input constraints. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics 37(2), 425–436 (2007)
Zhao, Y., Patek, S., Beling, P.: Decentralized Bayesian search using approximate dynamic programming methods. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics 38(4), 970–975 (2008)
Werbos, P.: Advanced forecasting methods for global crisis warning and models of intelligence. General Systems Yearbook 22, 25–38 (1977)
Zheng, C., Jagannathan, S.: Generalized Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman formulation-based neural network control of affine nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 19(1), 90–106 (2008)
Powell, W.: Approximate dynamic programming: solving the curses of dimensionality. Wiley, New York (2009)
He, P., Jagannathan, S.: Reinforcement learning neural-network-based controller for nonlinear discrete-time systems with input constraints. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics 37(2), 425–436 (2007)
Al-Tamimi, A., Lewis, F., Abu-Khalaf, M.: Model-free Q-learning designs for linear discrete-time zero-sum games with application to H-infinity control. Automatica 43, 473–481 (2007)
Vrabie, D., Pastravanu, O., Abu-Khalaf, M., Lewis, F.: Adaptive optimal control for continuous-time linear systems based on policy iteration. Automatica 45(2), 477–484 (2009)
Vamvoudakis, K., Lewis, F.: Online actor-critic algorithm to solve the continuous-time infinite horizon optimal control problem. Automatica 46(5), 878–888 (2010)
Murray, J., Cox, C., Lendaris, G., Saeks, R.: Adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C: Applications and Reviews 32(2), 140–153 (2002)
Wang, F., Jin, N., Liu, D., Wei, Q.: Adaptive dynamic programming for finite horizon optimal control of discrete-time nonlinear systems with ε-error bound. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 22(1), 24–36 (2011)
Zhang, H., Wei, Q., Liu, D.: An iterative adaptive dynamic programming method for solving a class of nonlinear zero-sum differential games. Automatica 47(1), 207–214 (2011)
Si, J., Wang, Y.: On-line learning control by association and reinforcement. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 12(2), 264–276 (2001)
Enns, R., Si, J.: Helicopter trimming and tracking control using direct neural dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 14(4), 929–939 (2003)
Zhang, H., Wei, Q., Luo, Y.: A novel infinite-time optimal tracking control scheme for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems via the greedy HDP iteration algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics 38(4), 937–942 (2008)
Zhang, H., Luo, Y., Liu, D.: Neural-network-based near-optimal control for a class of discrete-time affine nonlinear systems with control constraints. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 20, 1490–1503 (2009)
Wei, Q., Zhang, H., Dai, J.: Model-free multiobjective approximate dynamic programming for discrete-time nonlinear systems with general performance index functions. Neurocomputing 72(7-9), 1839–1848 (2009)
Wang, D., Liu, D., Wei, Q., Zhao, D.: Optimal control of unknown nonaffine nonlinear discrete-time systems based on adaptive dynamic programming. Automatica 48(8), 1825–1832 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Song, R., Xiao, W., Wei, Q. (2013). Neuro-control to Energy Minimization for a Class of Chaotic Systems Based on ADP Algorithm. In: Sun, C., Fang, F., Zhou, ZH., Yang, W., Liu, ZY. (eds) Intelligence Science and Big Data Engineering. IScIDE 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 8261. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-42057-3_78
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-42057-3_78
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-42056-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-42057-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)