Abstract
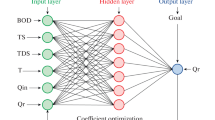
The dynamic behavior of an activated sludge system is highly complex and uncertain. To efficiently control and operate the system, a reliable model capable of accurately describing the several time-varying parallel processes of the system is needed. Most of the existing models are too complex to use for design or control purposes. This paper presents a feed-forward neural network model for the system. The model validation was achieved through the use of appropriate international accepted data of the benchmark simulation model no. 1 (BSM1). Simulation studies revealed that the neural network model exhibited an outstanding performance in predicting the effluent quality, root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.0464, mean absolute deviation (MAD) of 0.0347, correlation coefficient (R) of 0.979 for chemical oxygen demand (COD) and RMSE of 0.1103, MAD of 0.0794, R of 0.841 for the total nitrogen (TN) could be acheived. The model is quite effective and suitable tool for the activated sludge system.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henze, M., Gujer, W., Mino, T., Loosedrecht, V.: Activated Sludge Models ASM1, ASM2, ASM2D and ASM3. IWA Publishing, London (2000)
Gujer, W.: Activated Sludge Modelling: past, present and future. Water Science and Technology 53(3), 111–119 (2006)
Jeppson, U.: A Simplified Control-Oriented Model of the Activated Sludge Process. Mathematical Modelling of Systems 1(1), 3–16 (1995)
Tay, J., Zhang, X.: A Fast Predicting Neuro Fuzzy Model for High-Rate Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment Systems. Water Research 34(11), 2849–2860 (2000)
Gontarski, C., Rodrigues, P., Mori, M., Prenem, L.: Simualtion of an Industrial wastewater Treatment Plant using Artificial Neural Networks. Computers and Chemical Engineering 24, 1719–1723 (2000)
Oliveira-Esquerre, K., Mori, M., Bruns, R.: Simulation of an Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plant using Artificial Neural Networks and Principal Component Analysis. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering 19(4), 365–370 (2002)
Nasr, M., Moustafa, M., Seif, H., El-kobrosy, G.: Application of the Artificial Neural Network for the Prediction of El-agamy Wastewater Treatment Plant Performance-Egypt. Alexandria Engineering Journal 51, 37–43 (2012)
Mjalli, F., Al-Asheh, S., Al-Fadala, H.: Use of Artificial Neural Network Black Box Modelling for the Prediction of Wastewater Treatment Plants Performance. Journal of Environmental Management 83(3), 329–338 (2007)
Kriger, C., Tzenova, R.: Neural Networks for Prediction of Wastewater Treatment Plant Disturbance. In: 8th IEEE-Africon Conference, Windhoek, Namibia (2007)
Alex, J., Benedetti, L., Copp, J., Garnaey, K., Jeppson, U., Nopens, I., Pons, M., Rosen, C., Steyer, J., Vanrolleghem, P.: Benchmark Simulation Model no. 1. IWA publishing, London (2008)
McCulloch, W., Pitts, W.: A Logical Calculus of the Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity. Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics 5, 115–133 (1943)
Chiang, Y., Chang, L., Chang, F.: Comparison of Static feed-forward and Dyanmic Feedback Neural Networks for Rainfall-Runoff Modelling. Journal of Hydrology 290, 297–311 (2004)
Jain, A., Mao, J., Mohluddin, K.: Artificial Neural Networks: A Tutorial. IEEE-Computer Magazine 29(3), 31–44 (1996)
Rumelhart, D., Hinton, G., Williams, R.: Learning Internal Representations by Error Propagation. Parallel Distributed Processing 1, 318–362 (1986)
Hetch, N.: Kolmogorov’s Mapping Neural Network Existence Theorem. In: IEEE- First Annual International Conference on Neural Networks, New York (1987)
Rogers, L.L., Dowla, F.U.: Optimization of Groundwater Remediation using Artificial Neural Networks with Parallel Solute Transport Modelling. Water Resource Research 30(2), 457–481 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gaya, M.S., Wahab, N.A., Sam, Y.M., Samsuddin, S.I. (2013). Feed-Forward Neural Network Approximation Applied to Activated Sludge System. In: Tan, G., Yeo, G.K., Turner, S.J., Teo, Y.M. (eds) AsiaSim 2013. AsiaSim 2013. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 402. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-45037-2_63
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-45037-2_63
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-45036-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-45037-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)