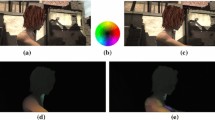
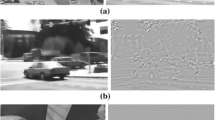
Abstract
The aim of this paper is to analyze the discontinuity preserving behavior of two methods in optical flow. With this objetive, we have implemented a well-known optical flow method that uses isotropic TV-L 1 regularization. For the second approach, we have modified this method, by adding a decreasing function in the regularization term, to avoid smoothing at flow discontinuities. As a consequence, we see a high improvement and a very accurate discontinuities detection in some sequences but not good enough in others. Adapting the weight of the decreasing function allows us to better define the flow discontinuities. Nevertheless, the experimental results show that the parameters that yield a good segmentation of the motion field, may also introduce important unstabilities. In this sense, the results seem promising, but it is very difficult to set a unified parameter configuration that works fine for all the sequences. We evaluate the performance of these approaches with some standard test sequences, such as the Middlebury benchmark database or the Yosemite sequence. Looking for the best parameters configuration, which provides the best contour definition, does not typically mean a solution which is closer to the ground truth.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvarez, L., Esclarín, J., Lefébure, M., Sánchez, J.: A pde model for computing the optical flow. In: XVI Congreso de Ecuaciones Diferenciales y Aplicaciones, C.E.D.Y.A. XVI, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, pp. 1349–1356 (1999)
Baker, S., Scharstein, D., Lewis, J.P., Roth, S., Black, M.J., Szeliski, R.: A database and evaluation methodology for optical flow. International Journal of Computer Vision 92(1), 1–31 (2011)
Brox, T., Bruhn, A., Papenberg, N., Weickert, J.: High accuracy optical flow estimation based on a theory for warping. In: Pajdla, T., Matas, J(G.) (eds.) ECCV 2004. LNCS, vol. 3024, pp. 25–36. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Horn, B.K.P., Schunck, B.G.: Determining optical flow. Artificial Intelligence 17, 185–203 (1981)
Nagel, H.H., Enkelmann, W.: An investigation of smoothness constraints for the estimation of displacement vector fields from image sequences. IEEE Transanctions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 8, 565–593 (1986)
Perona, P., Malick, J.: Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analasys and Machine Intelligence 12, 629–629 (1990)
Sánchez, J., Monzón, N., Salgado, A.: Robust Optical Flow Estimation. Image Processing On Line 2013, 242–260 (2013)
Wedel, A., Cremers, D., Pock, T., Bischof, H.: Structure- and motion-adaptive regularization for high accuracy optic flow. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1663–1668 (September 2009)
Xu, L., Jia, J., Matsushita, Y.: Motion detail preserving optical flow estimation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1293–1300 (June 2010)
Zach, C., Pock, T., Bischof, H.: A Duality Based Approach for Realtime TV-L 1 Optical Flow. In: Hamprecht, F.A., Schnörr, C., Jähne, B. (eds.) DAGM 2007. LNCS, vol. 4713, pp. 214–223. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Monzón López, N., Sánchez, J., Salgado de la Nuez, A. (2013). Optic Flow: Improving Discontinuity Preserving. In: Moreno-Díaz, R., Pichler, F., Quesada-Arencibia, A. (eds) Computer Aided Systems Theory - EUROCAST 2013. EUROCAST 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 8112. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-53862-9_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-53862-9_16
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-53861-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-53862-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)