Abstract
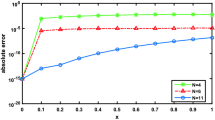
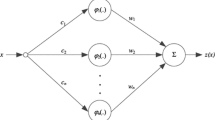
In this paper, we propose a numerical scheme to solve a kind of the nonlinear telegraph equation by using the Kansa’s method with Radial Basis Functions (RBFs). From the numerical results of experiments presented in this paper, we can get that the accuracy between the numerical solutions and the analytical solutions are valid. In this paper, we also give the analysis of the parameter c in IMQ radical basis function for the results.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lai, S.Y.: The asymptotic theory of solutions for a perturbed telegraph wave equation and its application. Appl. Math. Mech. 43(7), 657–662 (1997)
Kolesov, A.Y., Rozov, N.K.: Parametric excitation of high-mode oscillations for a non-linear telegraph equation. Sbornik Mathematics 191(7-8), 1147–1169 (2001)
Dehghan, M.: A numerical method for solving the hyperbolic telegraph equation. InterScience 24, 1080–1093 (2008)
Gao, F., Chi, C.: Unconditionally stable difference schemes for a one space dimensional linear hyperbolic equation. Appl. Math. Comput. 187, 1272–1276 (2007)
Alonso, J.M., Mawhi, J., Ortega, R.: Bounded solutions of second order semilinear evolution equations and applications to the telegraph equation. J. Math. Pures Appl. 78, 49–63 (1999)
Shang, Y.D.: Explicit and exact solutions for a class of nonlinear wave equations. Acta Math. Appl. Sinica 23, 21–30 (2000)
Fan, E.G., Zhang, H.Q.: The solitary wave solutions for a class of nonlinear wave equation. Chin. Phys. Soc. 46, 1245–1248 (1997)
Dehghan, M.: Parameter determination in a partial differential equation from the overspecified data. Math. Comput. Model. 41, 196–213 (2005)
Dehghan, M.: Implicit collocation technique for heat equation with non-classic initial condition. Int. J Non-Linear Sci. Numer. Simul. 7, 447–450 (2006)
Dehghan, M.: Finite difference procedures for solving a problem arising in modeling and design of certain optoelectronic devices. Math. Comput. Simulation 71, 16–30 (2006)
Liu, G.R., Gu, Y.T.: Boundary meshfree methods based on the boundary point methods. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 28, 475–487 (2004)
Jiang, T.S., Li, M., Chen, C.S.: The Method of Particular Solutions for Solving Inverse Problems of a Nonhomogeneous Convection-Diffusion Equation with Variable Coefficients. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A: Applications 61(5), 338–352 (2012)
Jiang, T.S., Jiang, Z.L., Jospeh, K.: A numerical method for one-dimensional time-dependent Schrodinger equation using radial basis functions. Internatioal Journal of Computational Methods (accepted, 2013)
Li, M., Jiang, T.S., Hon, Y.C.: A meshless method based on RBFs method for nonhomogeneous backward heat conduction problem. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements 34(9), 785–792 (2010)
Liu, G.R.: Mesh Free Method: Moving Beyond the Finite Element Methods. CRC Press, Florida (2002)
Liu, G.R., Liu, M.B.: Smooth Pariticle Hydrodynamics-a meshfree particle method. World Scientific, Singapore (2003)
Schaback, R.: Error estimates and condition numbers for radical basis function interpolation. J. Advances in Computational Mathematics 3(7), 251–264 (1995)
Wu, Z.M., Schaback, R.: Local error estimates for radical basis function interpolation of scattered data. J. IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis 13(1), 13–27 (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
De Su, L., Jiang, Z.W., Jiang, T.S. (2013). Numerical Solution for a Kind of Nonlinear Telegraph Equations Using Radial Basis Functions. In: Yang, Y., Ma, M., Liu, B. (eds) Information Computing and Applications. ICICA 2013. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 391. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-53932-9_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-53932-9_14
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-53931-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-53932-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)