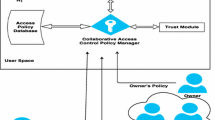
Abstract
Technology made socializing very simple and easy, connecting everyone is just a matter of a click today. The security of our personal information and sharing that information in the digital world has always been a major challenge for the ever-growing social networks. When it comes to the relationship between people and technology, the attribution of trust is a matter of dispute always. This paper proposes an access control scheme called Trust Based Access Control for Social Networks, or STBAC, which allows users to share data among their friends, using a trust computation to determine which friends should be given access. This trust computation uses previous interactions among a user’s friends to classify his or her peers into privileged or unprivileged zones, which determine whether that peer gains access to the user’s data. The system will work as a filter for each of the peer and try to evaluate the trust access control in social networks.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Omanakuttan, S., Chatterjee, M.: Trust Based Access Control for Social Networks(STBAC). International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology (IJIET ), 325–331 (February 1, 2013)
Li, X., Ling, L.: PeerTrust: supporting reputation-based trust for peer-to-peer electronic communities. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 16(7), 843–857 (2004)
Ma, X., Feng, Z., Xu, C., Wang, J.: A Trust-Based Access Control with Feedback. In: 2008 International Symposiums on Information Processing (ISIP), May 23-25, pp. 510–514 (2008)
Yang, R., Lin, C., Jiang, Y., Chu, X.: Trust Based Access Control in Infrastructure-Centric Environment. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), June 5-9, pp. 1–5 (2011)
Poniszewska-Maranda, A.: Platform for Access Control Management in Information System Based on Extended RBAC Model. In: 2010 12th International Symposium on Symbolic and Numeric Algorithms for Scientific Computing (SYNASC), pp. 510–517 (September 2010)
Lampson, B.: Protection. In: Proceedings of the 5th Annual Princeton Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, pp. 437–443. Princeton University (1971)
Benantar, M.: Access Control Systems: Security, Identity Management and Trust Models. Springer, New York (2006)
Sandhu, R.S., Coyne, E.J., Feinstein, H.L., Youman, C.E.: Role-based access control models. IEEE Computer 29(2), 38–47 (1996)
Carminati, B., Ferrari, E., Perego, A.: Rule-based access control for social networks. In: Meersman, R., Tari, Z., Herrero, P. (eds.) OTM 2006 Workshops, Part II. LNCS, vol. 4278, pp. 1734–1744. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Galpin, R., Flowerday, S.V.: Online social networks: Enhancing user trust through effective controls and identity management. In: Information Security South Africa (ISSA), August 15-17, pp. 1–8 (2011)
Wang, H., Sun, L.: Trust-Involved Access Control in Collaborative Open SociaNetworks. In: 2010 4th International Conference on Network and System Security (NSS), September 1-3, pp. 239–246 (2010)
Graffi, K., Mukherjee, P., Menges, B., Hartung, D., Kovacevic, A., Steinmetz, R.: Practical security in p2p- based social networks. In: IEEE 34th Conference on Local Computer Networks, LCN 2009, October 20-23, pp. 269–272 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Omanakuttan, S., Chatterjee, M. (2014). Experimental Analysis on Access Control Using Trust Parameter for Social Network. In: Martínez Pérez, G., Thampi, S.M., Ko, R., Shu, L. (eds) Recent Trends in Computer Networks and Distributed Systems Security. SNDS 2014. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 420. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-54525-2_49
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-54525-2_49
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-54524-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-54525-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)