Abstract
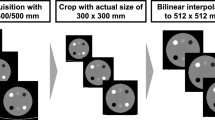
In this work, we propose a U-Net-based super-resolution neural network, SRU-Net, to create emulated high spatial resolution (eHR) CT images from low spatial resolution (LR) CT images. As resolution could be defined by the modulation transfer function in CT reconstruction, we propose the novel approach based on CT reconstruction kernels to create realistic multi-detector CT (MDCT) synthetic LR images from high-resolution cone-beam CT (CBCT) scans. Keeping a constant sampling grid size of 0.20 × 0.20mm2, we reconstruct two types of MDCT-like LR images and one corresponding HR image from the same CBCT raw data and train two models respectively. We validated the performance of the trained models on unseen LR CBCT images. We then applied the trained network to MDCT images. Mean squared error, structural similarity index measures and peak signal-to-noise ratio of two models show significant improvements (p < 0.001) in the eHR images.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbosa Jr EJM, Gefter WB, Ghesu FC, Liu S, Mailhe B, Mansoor A et al. Automated detection and quantification of COVID-19 airspace disease on chest radiographs: a novel approach achieving expert radiologist-level performance using a deep convolutional neural network trained on digital reconstructed radiographs from computed tomography-derived ground truth. Invest Radiol. 2021;56(8):471–9.
Umehara K, Ota J, Ishida T. Application of super-resolution convolutional neural network for enhancing image resolution in chest CT. J Digit Imaging. 2018;31(4):441–50.
Park J, Hwang D, Kim KY, Kang SK, Kim YK, Lee JS. Computed tomography superresolution using deep convolutional neural network. Phys Med Biol. 2018;63(14):145011.
Yu H, Liu D, Shi H, Yu H, Wang Z, Wang X et al. Computed tomography super-resolution using convolutional neural networks. Conf Proc IEEE Int Conf Signal Image Process Appl. IEEE. 2017:3944–8.
Parker JA, Kenyon RV, Troxel DE. Comparison of interpolating methods for image resampling. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1983;2(1):31–9.
Hirahara D, Takaya E, Kadowaki M, Kobayashi Y, Ueda T. Effect of the pixel interpolation method for downsampling medical images on deep learning accuracy. J. comput. commun. 2021;9(11):150–6.
Grunz JP, Weng AM, Gietzen CH, Veyhl-Wichmann M, Pennig L, Kunz A et al. Evaluation of ultra-high-resolution cone-beam CT prototype of twin robotic radiography system for cadaveric wrist imaging. Acad Radiol. 2021;28(10):e314–e322.
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. Springer. 2015:234–41.
Paszke A, Gross S, Massa F, Lerer A, Bradbury J, Chanan G et al. PyTorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32. Ed. byWallach H, Larochelle H, Beygelzimer A, d’Alché-Buc F, Fox E, Garnett R. Curran Associates, Inc., 2019:8024–35.
Peng C, Zhou SK, Chellappa R. DA-VSR: domain adaptable volumetric super-resolution for medical images. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. Springer. 2021:75–85.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Der/die Autor(en), exklusiv lizenziert an Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, ein Teil von Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fok, W.Y.R. et al. (2023). Cross-modality Training Approach for CT Super-resolution Network. In: Deserno, T.M., Handels, H., Maier, A., Maier-Hein, K., Palm, C., Tolxdorff, T. (eds) Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2023. BVM 2023. Informatik aktuell. Springer Vieweg, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-41657-7_66
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-41657-7_66
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer Vieweg, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN: 978-3-658-41656-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-658-41657-7
eBook Packages: Computer Science and Engineering (German Language)