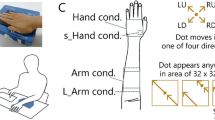
Abstract
Background: Sliding of surfaces across the skin changes the position of edges and texture elements relative to the receptive fields of somatosensory neurons. This ‘successive positions’ cue is sufficient to elicit motion sensation. Surfaces also create lateral skin stretch due to friction and we ask whether this potential cue influences perceived direction. Method: A 4-pin array was applied to the forearm to manipulate the two motion cues independently. It indicated distal or proximal direction by pin activation in the order 1-2-3-4 or 4-3-2-1. Crucially, each pin also stretched the skin by moving 3.5 mm laterally in the same (Congruent cues) or opposite direction (Incongruent cues). Results: 90 % of motion direction judgments accurately reflected succession of positions with a Congruent skin stretch cue but only 79 % with an Incongruent skin stretch cue (F1,7 = 6.80, p = .035). Conclusion: The skin stretch cue contributes to neural coding of motion direction.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bice, R.C.: Apparent movement in vibrotactile displays. Percept. Mot. Skills 29(2), 575–578 (1969)
Kirman, J.H.: Tactile apparent movement: the effects of number of stimulators. J. Exp. Psychol. 103(6), 1175–1180 (1974)
Gardner, E.P., Sklar, B.F.: Discrimination of the direction of motion on the human hand: a psychophysical study of stimulation parameters. J. Neurophysiol. 71(6), 2414–2429 (1994)
Whitsel, B.L., Dreyer, D.A., Hollins, M., Young, M.G.: The coding of direction of tactile stimulus movement. In: Kenshalo, D. (ed.) Sensory Functions of the Skin of Humans, pp. 79–107. Springer, US. doi:10.1007/978-1-4613-3039-4_6 (1979)
Olausson, H., Wessberg, J., Kakuda, N.: Tactile directional sensibility: peripheral neural mechanisms in man. Brain Res. 866(1–2), 178–187 (2000)
Whitsel, B.L., Roppolo, J.R., Werner, G.: Cortical information processing of stimulus motion on primate skin. J. Neurophysiol. 35, 691–717 (1972)
Gould, W.R., Vierck Jr, C.J., Luck, M.M.: Cues for supporting recognition of the orientation or direction of movement of tactile stimuli. In: Kensalo, D.R. (ed.) Sensory functions of the skin of humans, pp. 63–78. Plenum Press, New York (1979)
Essick, G.K.: Factors affecting direction discrimination of moving tactile stimuli. In: Morley, J.W. (ed.) Neural aspects in tactile sensation, pp. 1–54. North-Holland Elsevier Science, Amsterdam (1998)
Olausson, H., Norrsell, U.: Observations on human directional sensibility. J. Physiol. 464, 545–559 (1993)
Macmillan, N.A., Creelman, D.: Detection Theory: A User’s Guide. Lawrence Erlbaum Asssociates, Mahwah (2005)
R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, (Vienna, Austria). ISBN:3-900051-07-0 (2010). http://www.R-project.org
Wickham, H.: ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Springer, Dordrecht (2009)
Cousineau, D.: Confidence intervals in within-subject designs: A simpler solution to Loftus and Masson’s method. Tutor. Quant. Methods Psych. 1, 42–45 (2005)
Morey, R.D.: Confidence intervals from normalized data: a correction to cousineau (2005). Tutor. Quant. Methods Psych. 4(2), 61–64 (2008)
Bicchi, A., Dente, D., Scilingo, E.P.: Haptic Illusions induced by Tactile Flow. In: Proceedings of Eurohaptics, pp. 314–329 (2003)
Vallbo, A., Olausson, H., Wessberg, J., Kakuda, N.: Receptive field characteristics of tactile units with myelinated afferents in the hairy skin of human subjects. J. Physiol. (London) 483, 783–795 (1995)
Olausson, H., Wessberg, J., Kakuda, N.: Tactile directional sensibility: peripheral neural mechanisms in man. Brain Res. 866(1–2), 178–187 (2000)
Whitsel, B.L., Franzen, O., Dreyer, D.A., Hollins, M., Young, M., Essick, G.K., Wong, C.: Dependence of subjective traverse length on velocity of moving tactile stimuli. Somatosens. Res. 3(3), 185–196 (1986)
Acknowledgements
We thank Timothy Turner and Raymond Patton for designing and making the apparatus, and Juno Kim for the software. This study was supported by Australian Research Council Discovery grant DP110104691 to TSC and IB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Seizova-Cajic, T., Karlsson, K., Bergstrom, S., McIntyre, S., Birznieks, I. (2014). Lateral Skin Stretch Influences Direction Judgments of Motion Across the Skin. In: Auvray, M., Duriez, C. (eds) Haptics: Neuroscience, Devices, Modeling, and Applications. EuroHaptics 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 8618. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-44193-0_53
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-44193-0_53
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-44192-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-44193-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)